What is depreciation?
Remembering depreciation concept, it is a gradual attribution of the asset cost to expenses over its useful life. Different depreciation methods can be applied.
Double Declining Balance Method of Depreciation
In certain cases businesses do use double declining balance method of depreciation to attribute cost of property, plant and equipment to expenses.
When this method is applied, in the first years of depreciation bigger part of the cost value for the asset is attributed to expenses, gradually declining over the useful life of the asset.
 Such method is supported in case the asset actually depreciated more during its first years of usage
Such method is supported in case the asset actually depreciated more during its first years of usage
Also in certain cases such method is allowed to defer recognition of profit to later periods, for example for corporate income tax purposes.
Double Declining Balance Formula
Here is double declining balance formula:
Double Declining Balance Depreciation – Example
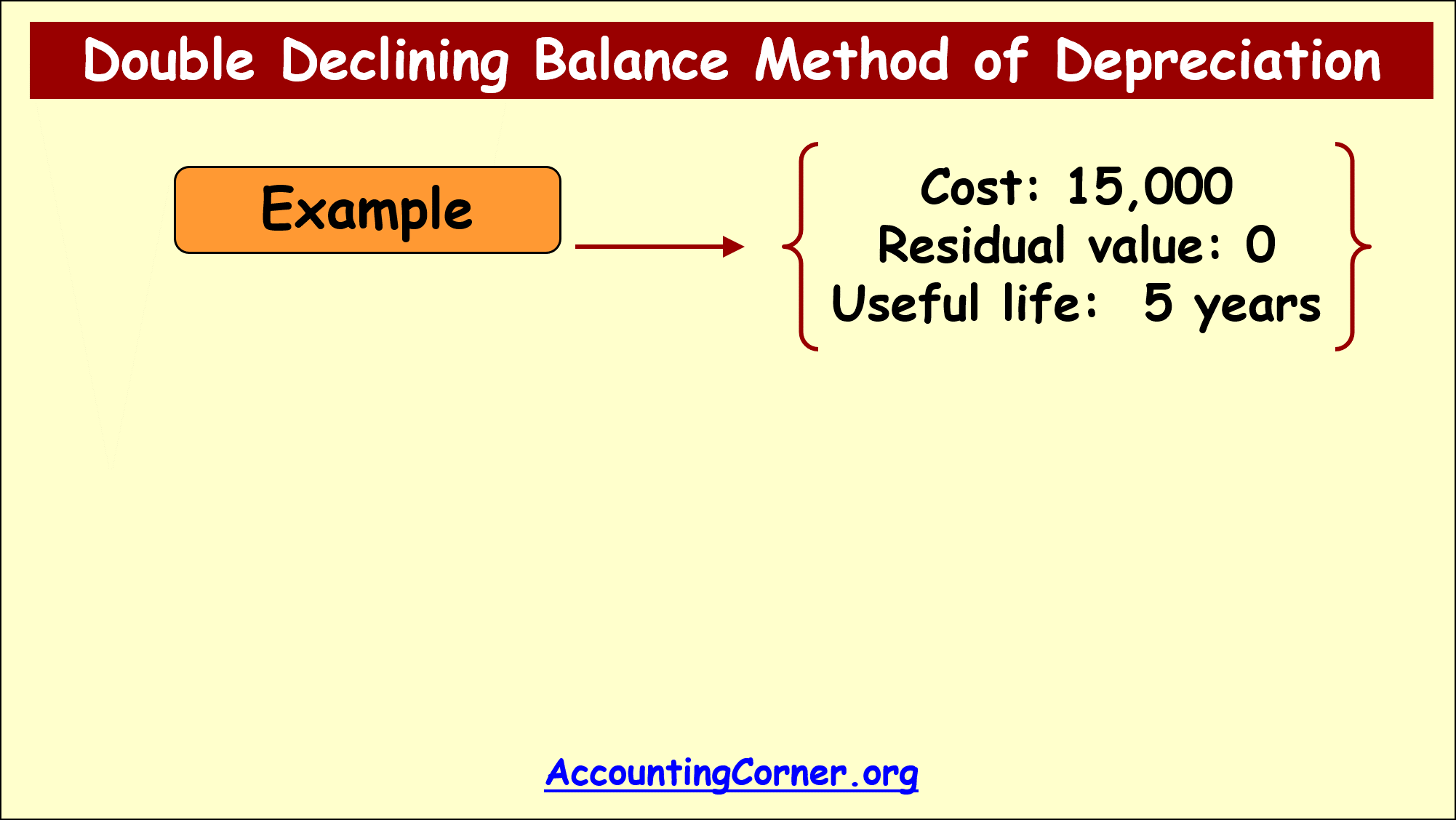
In order to demonstrate application of double declining balance method of depreciation explore the below example:
- Asset cost 15,000
- Residual value 0
- Useful life 5 years
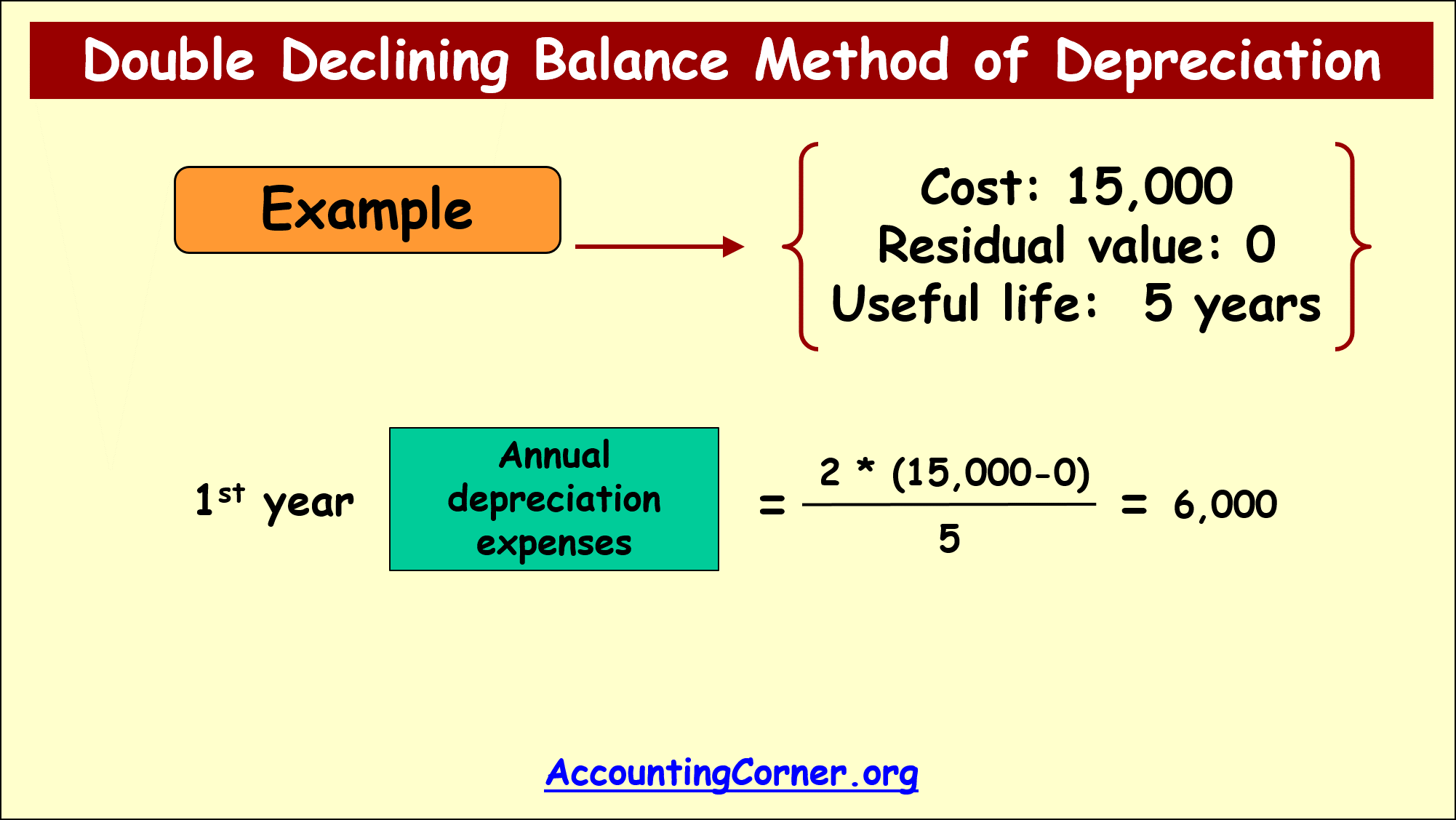
 1st year annual depreciation=2*(15,000-0)/5=6,000
1st year annual depreciation=2*(15,000-0)/5=6,000
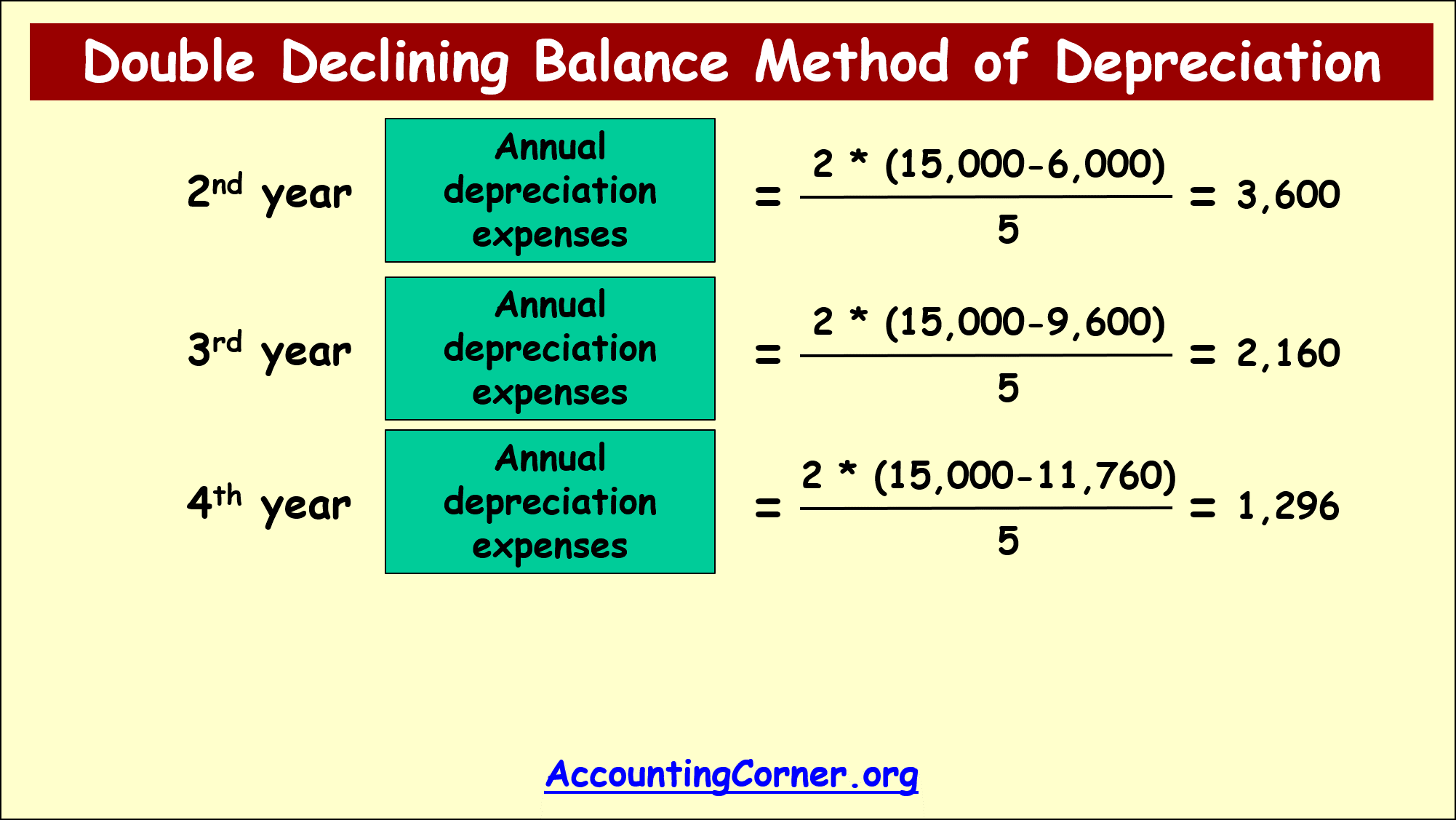
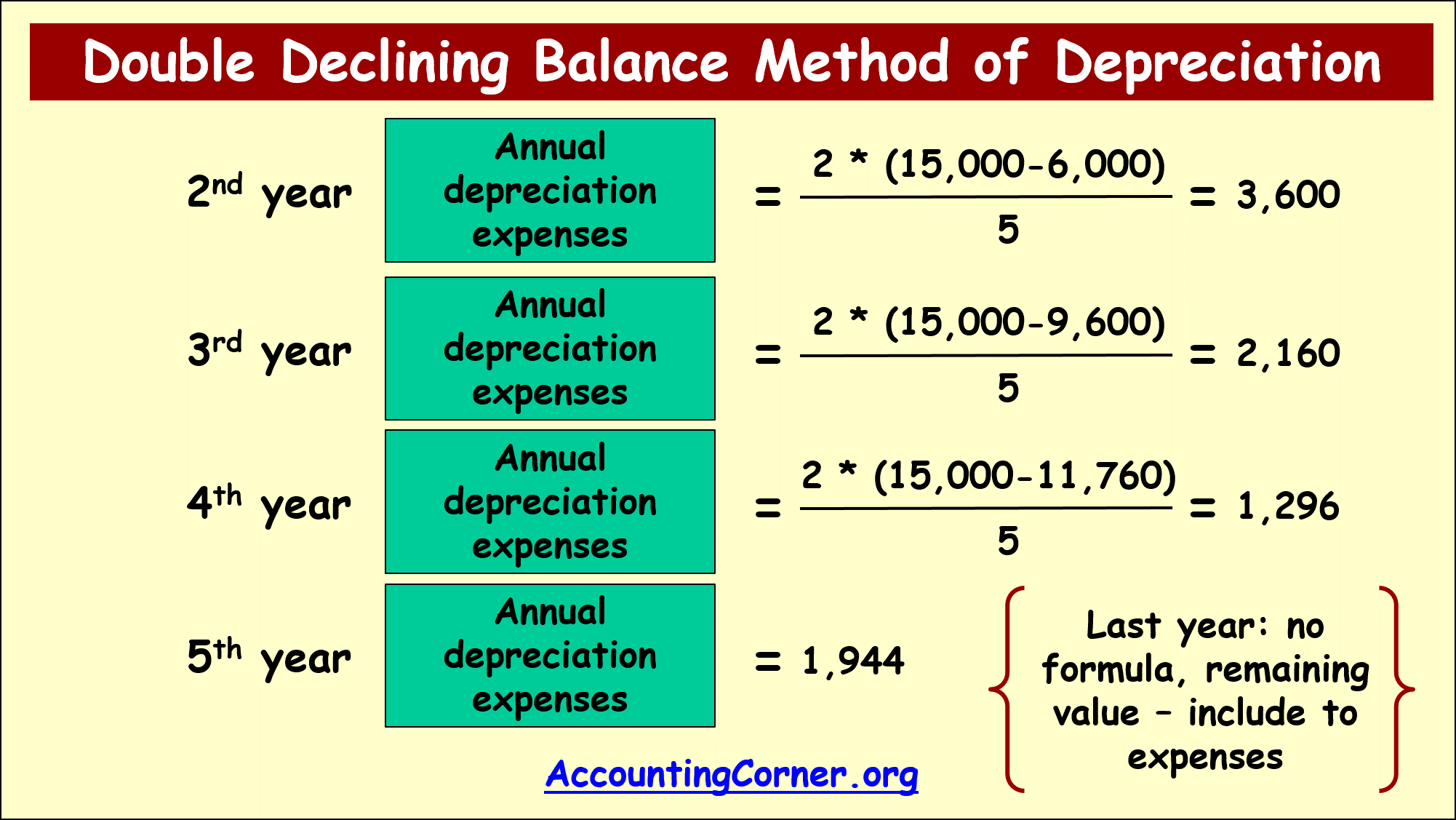
 2nd year annual depreciation=2*(15,000-6,000)/5=3,600
2nd year annual depreciation=2*(15,000-6,000)/5=3,600
 3rd year annual depreciation=2*(15,000 – (6,000+3,600))/5=2,160
3rd year annual depreciation=2*(15,000 – (6,000+3,600))/5=2,160
 4th year annual depreciation=2*(15,000-(6,000+3,600+2,160))/5=1,296
4th year annual depreciation=2*(15,000-(6,000+3,600+2,160))/5=1,296
 5th year annual depreciation=1,944
5th year annual depreciation=1,944
From this example it is obvious, that over the 5 years useful life of the asset in the beginning depreciation is much higher comparing to later years.

Over the last year no formula is applied, since the remaining book value is attributed to depreciation expenses.
Double Declining Balance Method of Depreciation – Video
Visual Presentation
Return from Double Declining Balance Method of Depreciation to AccountingCorner.org