What is the meaning of incurred?
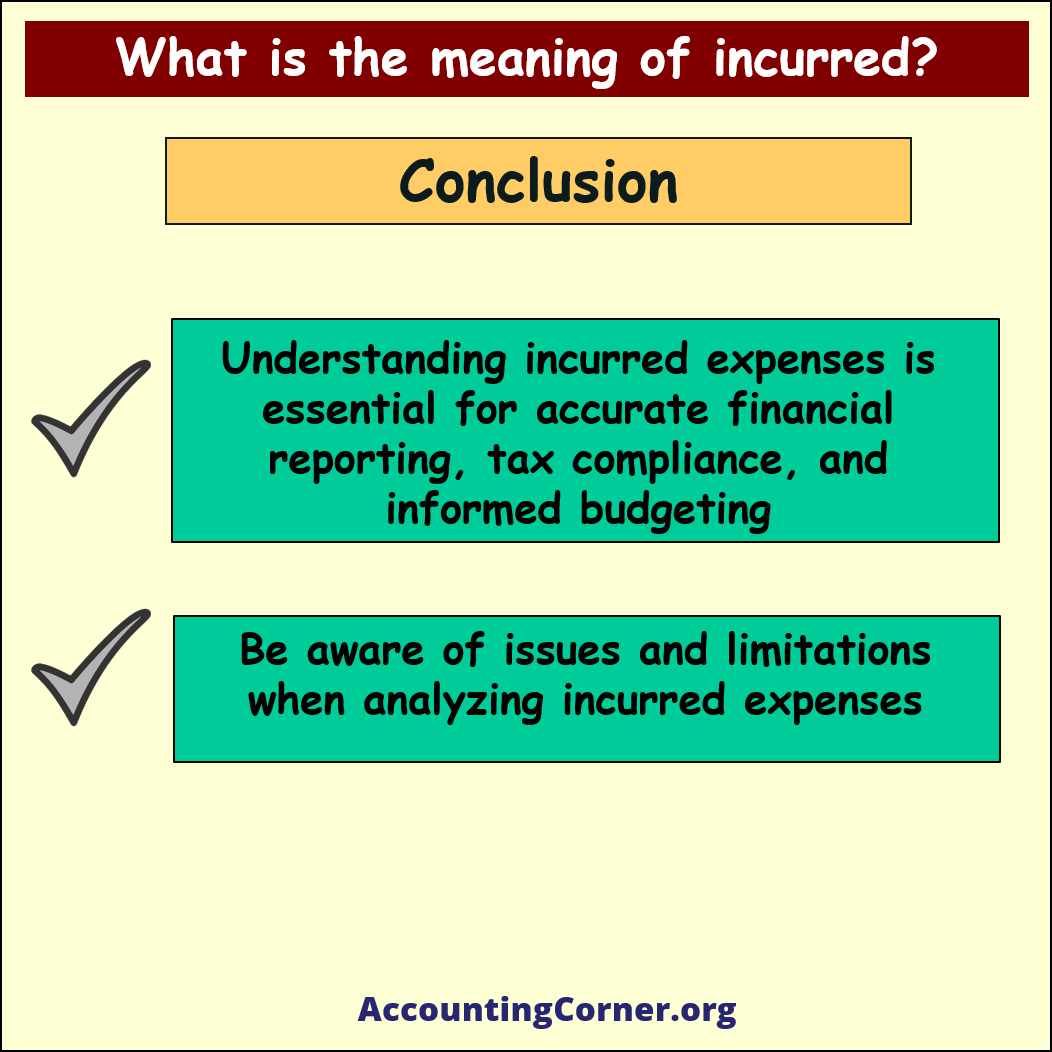
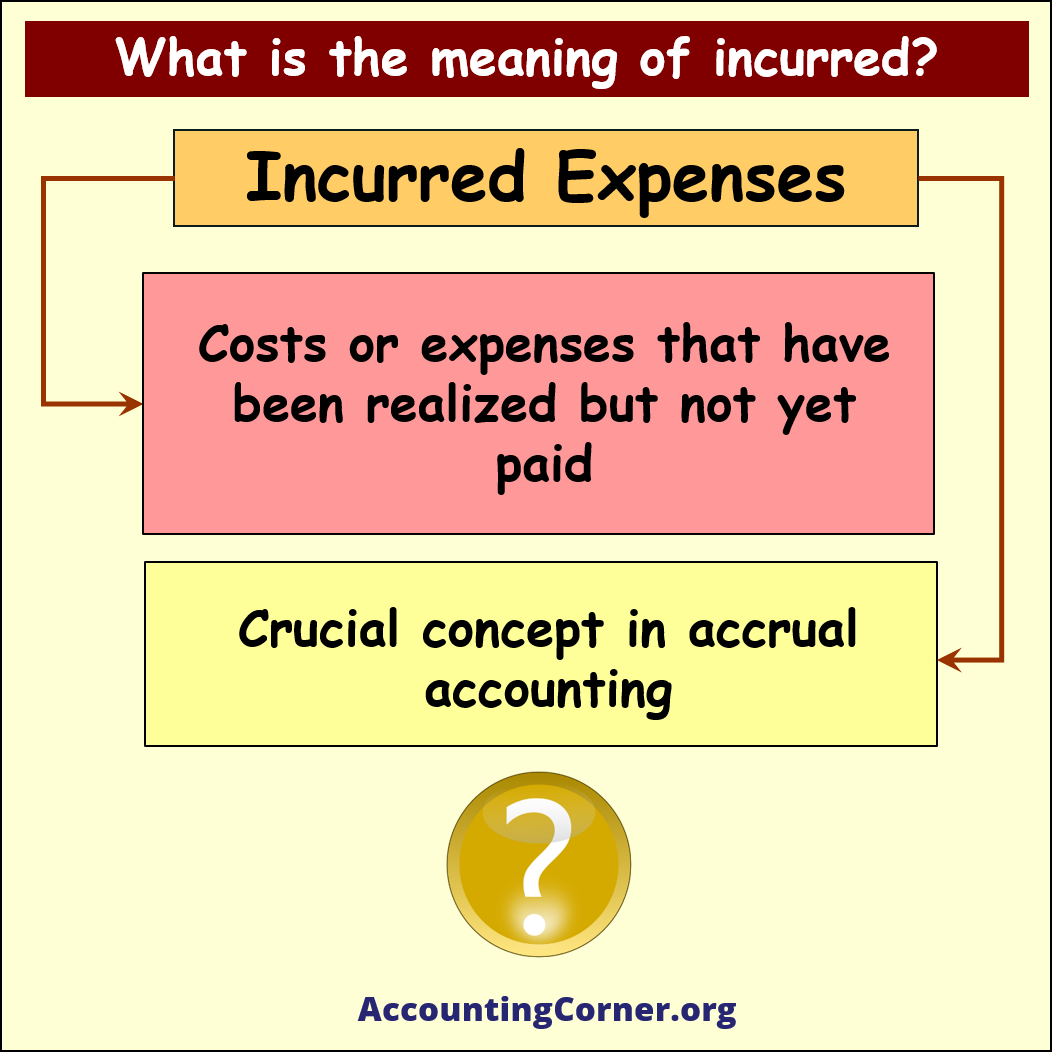
In accounting and finance, “incurred” refers to the recognition of a cost or expense that has been realized but not yet paid. This concept is crucial in accrual accounting, which records financial transactions when they are incurred rather than when they are paid or received.
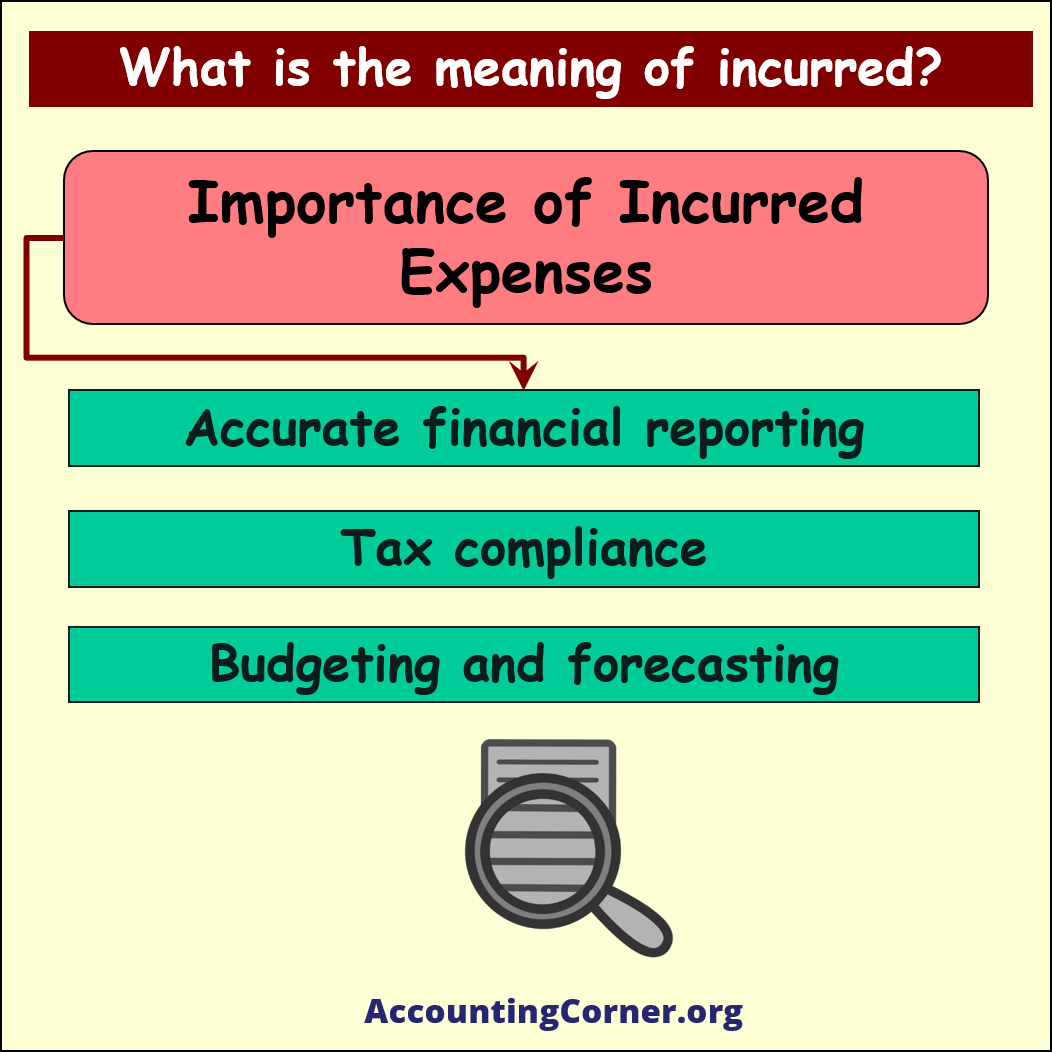
Importance of incurred:
- Accurate financial reporting: Recognizing incurred expenses helps businesses provide an accurate picture of their financial performance and health, as it ensures all costs associated with the reporting period are accounted for, regardless of when they are paid.
- Tax compliance: Recognizing incurred expenses is essential for tax compliance, as it helps businesses accurately calculate their taxable income and ensure they are paying the appropriate amount of taxes.
- Budgeting and forecasting: Recognizing incurred expenses is necessary for effective budgeting and financial planning, as it allows businesses to make informed decisions based on their actual financial performance.
Types of incurred:
- Incurred but not reported (IBNR): These are expenses that have been incurred but have not yet been reported or recorded in the company’s financial statements. IBNR expenses are common in the insurance industry, where claims may not be reported immediately after an event occurs.
- Incurred and reported: These are expenses that have been both incurred and reported in the financial statements. They are recognized in the company’s accounting records during the period in which they are incurred.
Examples of incurred:
- Salaries: Employees earn salaries throughout a given pay period, but they may not be paid until the end of that period. The salary expenses are incurred as the employees work, even if they haven’t been paid yet.
- Utilities: A company may use electricity, gas, and water during a month but not receive the bill until the following month. The expenses for utilities are incurred during the month of usage, even if they haven’t been paid yet.
- Depreciation: Depreciation represents the gradual wear and tear of an asset over time. Though no cash is paid out for depreciation, it’s considered an incurred expense as it reflects the reduction in the asset’s value over time.
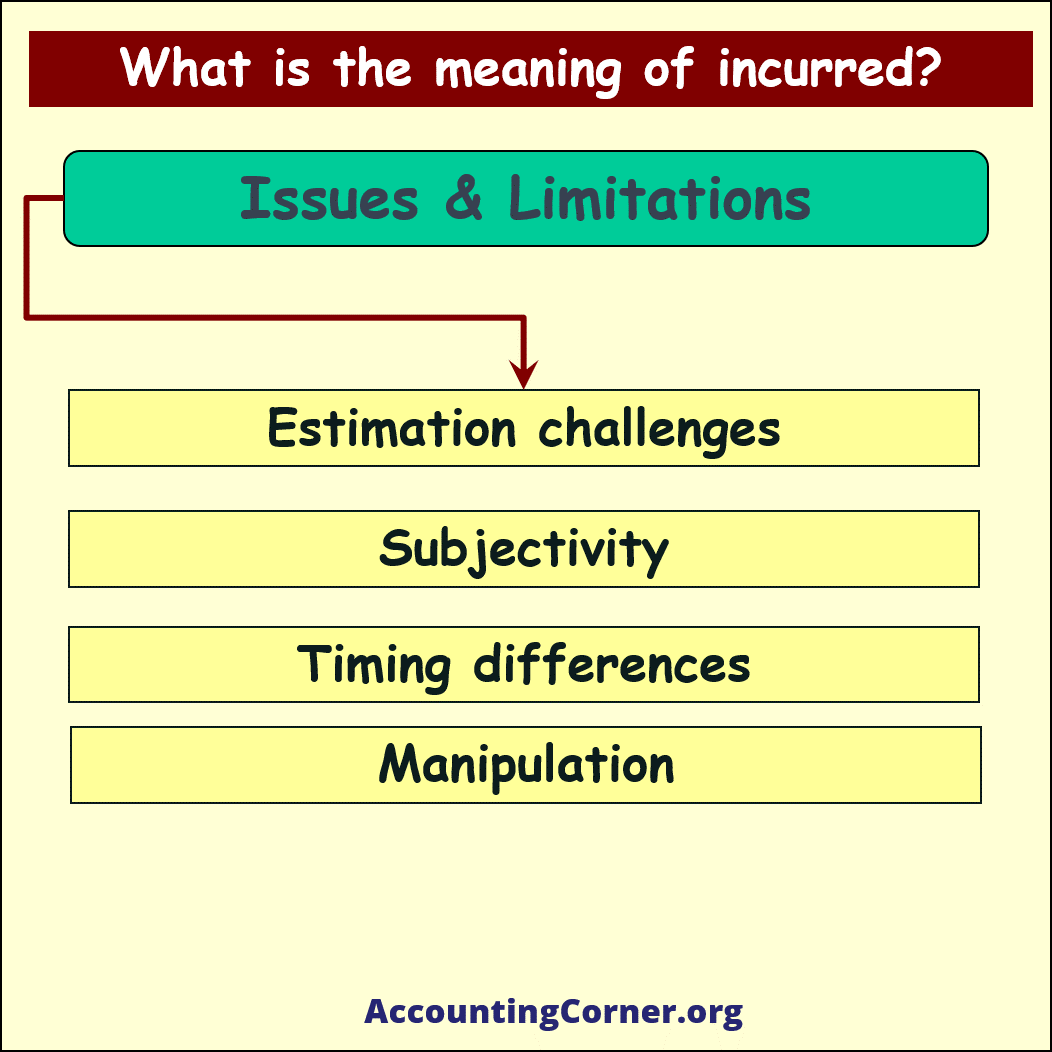
Issues and limitations of incurred:
- Estimation: Accurately estimating incurred expenses can be challenging, especially for those that are not easily quantifiable, like IBNR claims in the insurance industry.
- Subjectivity: The process of recognizing incurred expenses can be subjective, as different companies may have different interpretations of when an expense is truly incurred.
- Timing differences: Accrual accounting can result in timing differences between when expenses are recognized and when they are paid, which may create cash flow management challenges.
- Manipulation: Businesses may manipulate the recognition of incurred expenses to present a better financial picture, which can mislead investors and other stakeholders.
Visual material
Video: What is the meaning of incurred?
Return from Incurred Meaning to AccountingCorner.org home