What is the meaning of EBITA?
 EBITA meaning: EBITA is a financial metric, that measures business earnings before accounting for interest, taxes and amortization. It is used to evaluate business operational efficiency and profitability.
EBITA meaning: EBITA is a financial metric, that measures business earnings before accounting for interest, taxes and amortization. It is used to evaluate business operational efficiency and profitability.

What Does EBITA Stand For?
 EBITA full form: Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, and Amortization.
EBITA full form: Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, and Amortization.
It is a financial metric used to measure business operating performance by examining its earnings before considering the effects of interest, taxes, and amortization.
EBITA helps investors and analysts assess a company’s profitability and efficiency by focusing on its core operations.

Importance of EBITA
- EBITA is important because it provides insights into business operational efficiency, allowing for comparisons between companies or industries with different capital structures, tax rates, and levels of intangible assets.
- It is useful for valuing companies, analyzing potential acquisitions, or evaluating business performance over time.
Formula for EBITA
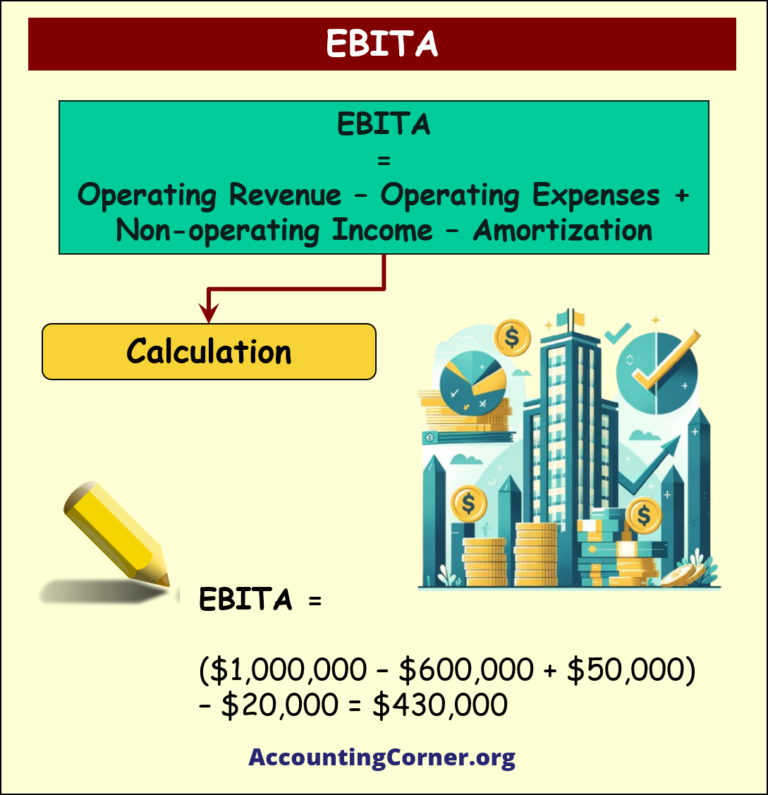
 The following formula is used to calculate EBITA:
The following formula is used to calculate EBITA:
EBITA Calculation Example
 Suppose a company has the following financial information:
Suppose a company has the following financial information:
- Operating Revenue: $1,000,000
- Operating Expenses: $600,000
- Non-operating Income: $50,000
- Amortization: $20,000
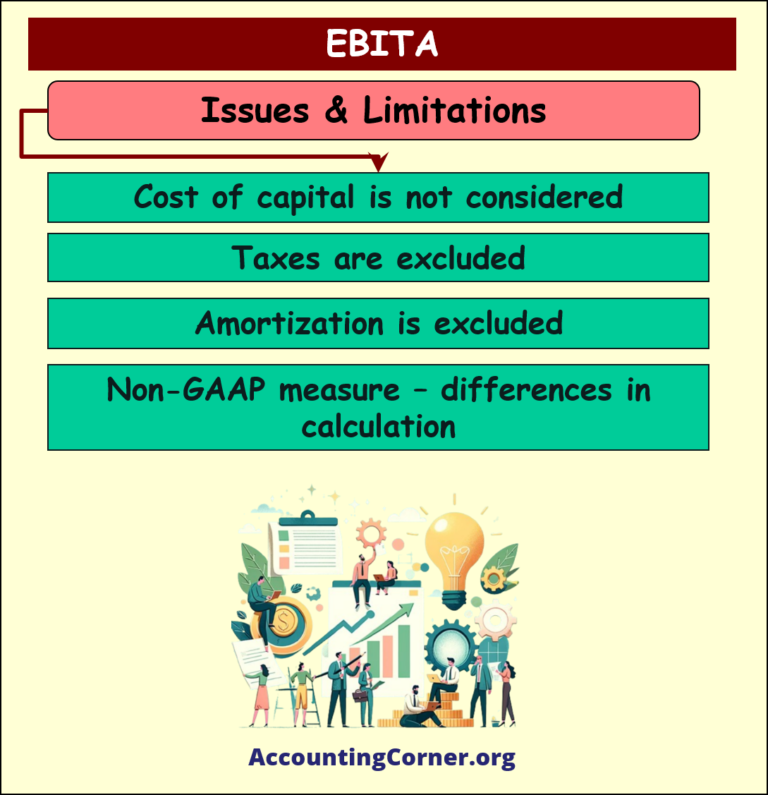
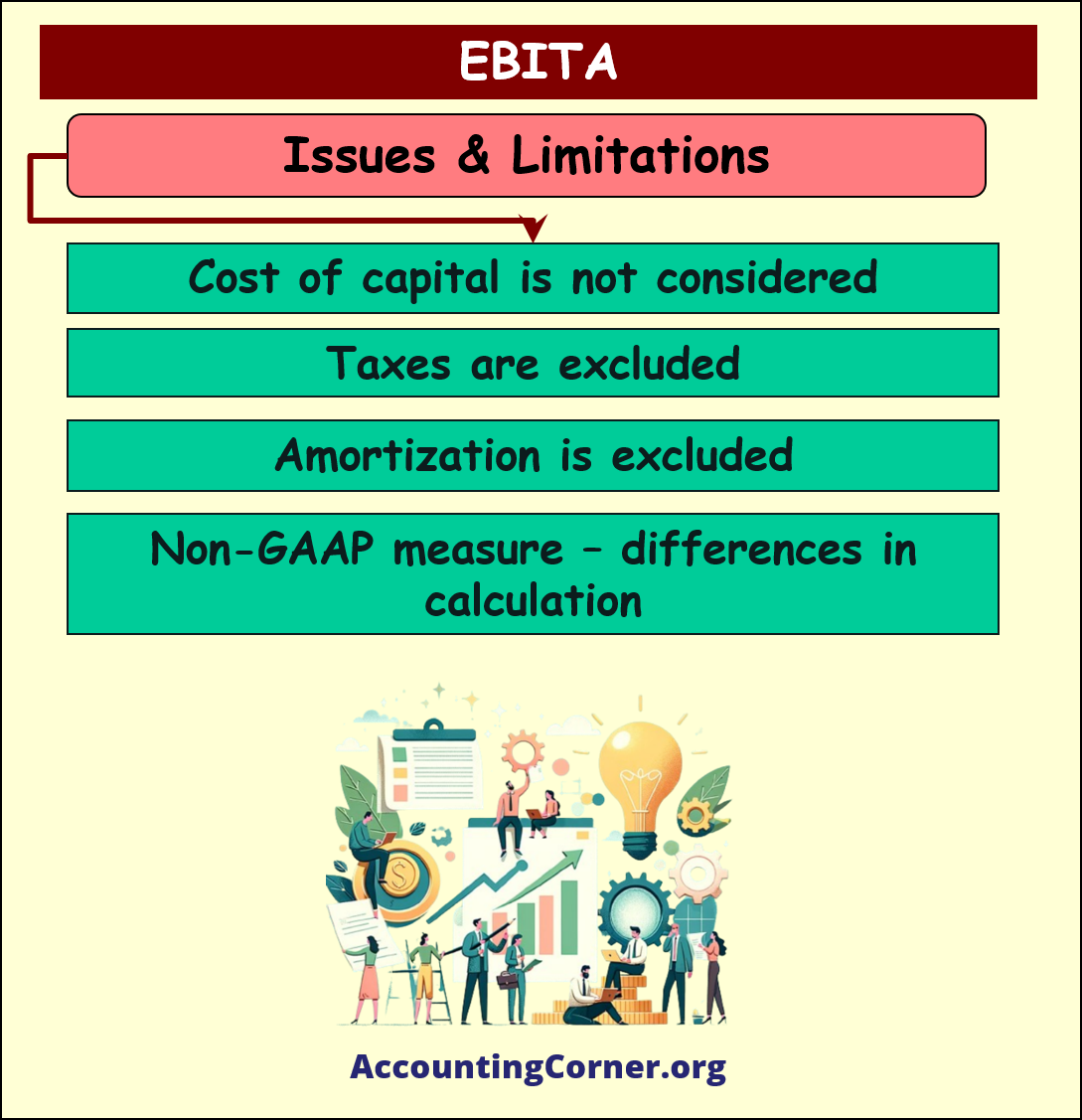
Issues and Limitations of EBITA
- EBITA does not consider the cost of capital (interest expense) and can therefore overstate a company’s performance if it has high debt levels.
- It also excludes taxes, which can vary significantly between companies and jurisdictions, leading to misleading comparisons.
- Amortization is excluded, which can make companies with significant intangible assets appear more profitable than they are.
- EBITA is a non-GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) measure, meaning it can be calculated differently by different companies, reducing comparability.
EBITDA & EBITA Comparison – When to use each metrics?
- EBITA 📌📌 Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, and Amortization
- EBITDA 📌📌 Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization
These both financial metrics used to evaluate business operating performance. However, they differ in terms of the expenses they exclude:
 EBITA:
EBITA:
-
- Definition: EBITA is a company’s earnings before interest, taxes, and amortization of intangible assets are deducted.
- Use: EBITA is used, when the focus is on operating performance, while considering depreciatio, but excluding the amortization of intangible assets. It’s particularly useful for businesses with significant intangible assets, such as intellectual property, goodwill, or patents. This metric provides a clearer picture of the company’s operational efficiency without the impact of non-cash amortization charges.
 EBITDA:
EBITDA:
-
- Definition: EBITDA is a company’s earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization are deducted.
- Use: EBITDA is widely used to assess business overall financial performance, excluding the effects of capital structure, tax rates, and non-cash accounting items like depreciation and amortization. It’s a popular metric for comparing profitability between businesses and industries, because it eliminates the effects of financing and accounting decisions.
When to Use Each Metric?
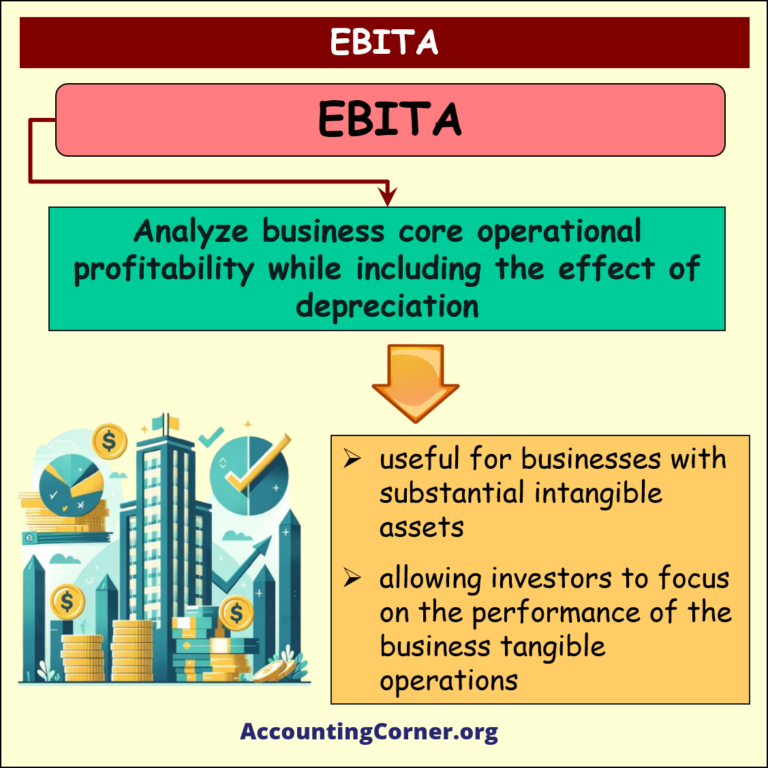
🚩EBITA:
-
- Use EBITA when you want to analyze business core operational profitability, while including the effect of depreciation (which reflects the physical asset usage), but excluding the effect of amortization of intangibles.
- It is particularly useful for companies with substantial intangible assets, allowing investors to focus on the performance of the company’s tangible operations.
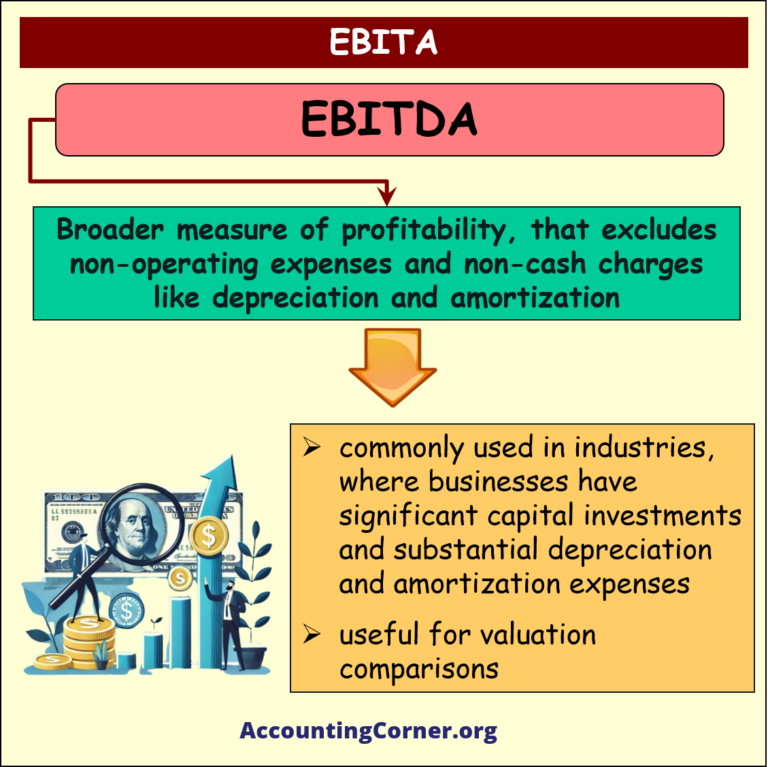
🚩EBITDA:
-
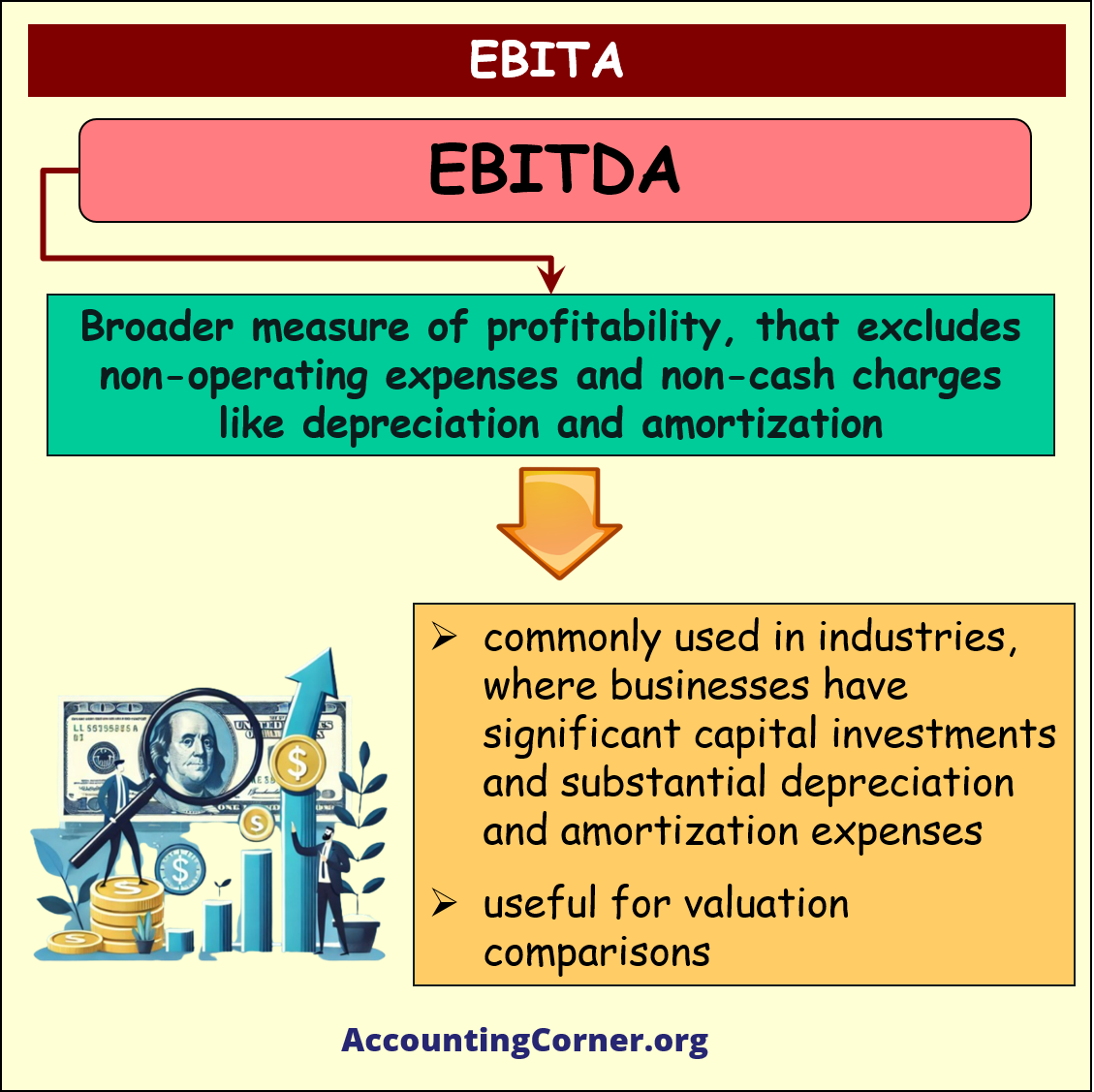
- Use EBITDA for a broader measure of profitability, that excludes non-operating expenses and non-cash charges like depreciation and amortization.
- This metric is commonly used in industries where companies have significant capital investments and substantial depreciation and amortization expenses.
- It’s also useful for valuation comparisons, especially in mergers and acquisitions, as it provides a clearer picture of operational profitability without the impact of varying capital structures and tax environments.
EBITA – Video Material
EBITA – Visual Material
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from EBITA Meaning to AccountingCorner.org home