Double Entry Accounting is a crucial concept in the field of accounting and finance, particularly important for readers of a blog focused on these topics. Here’s a detailed explanation covering various aspects of this subject:
- Definition of Double Entry Accounting:
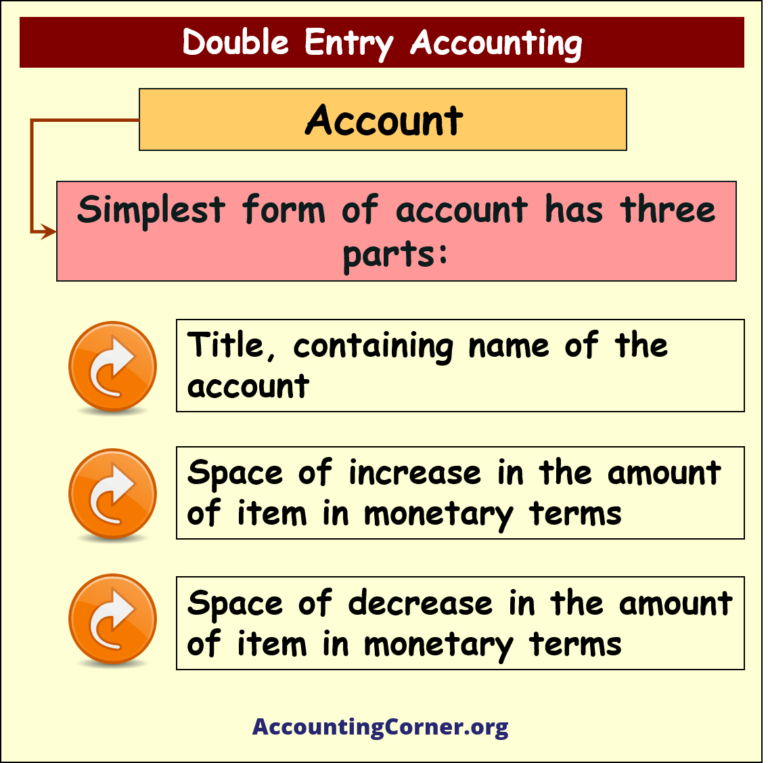
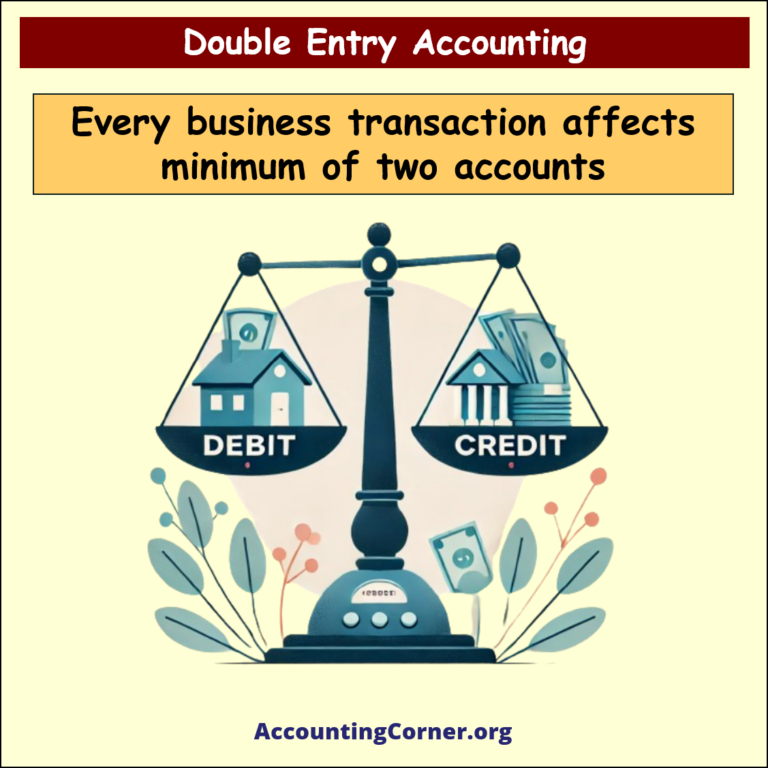
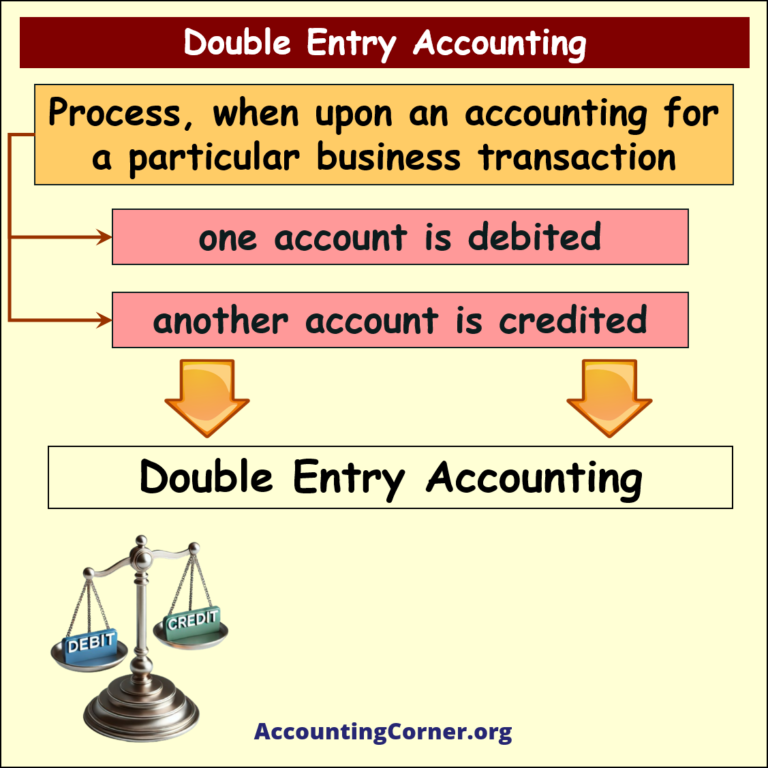
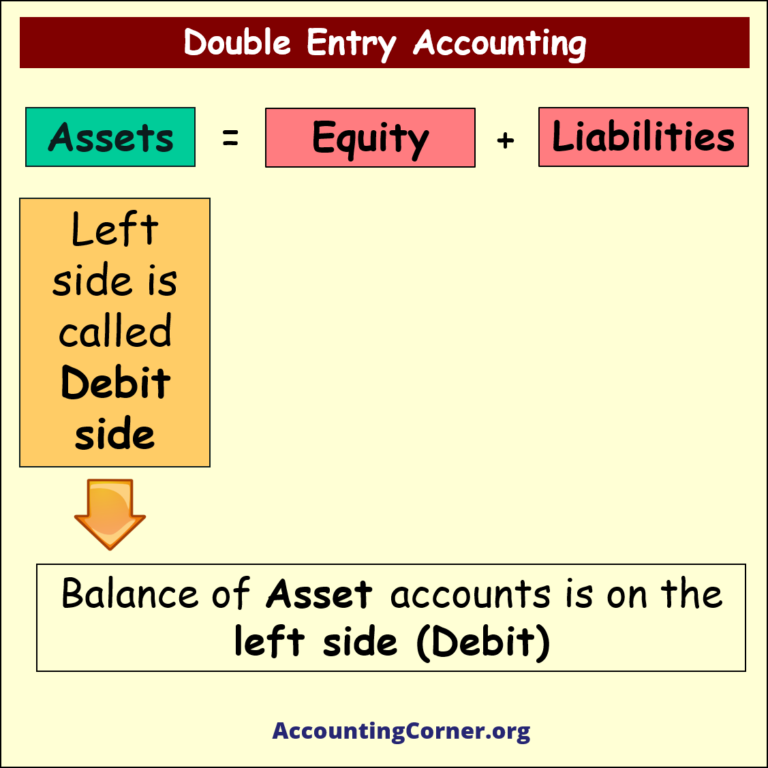
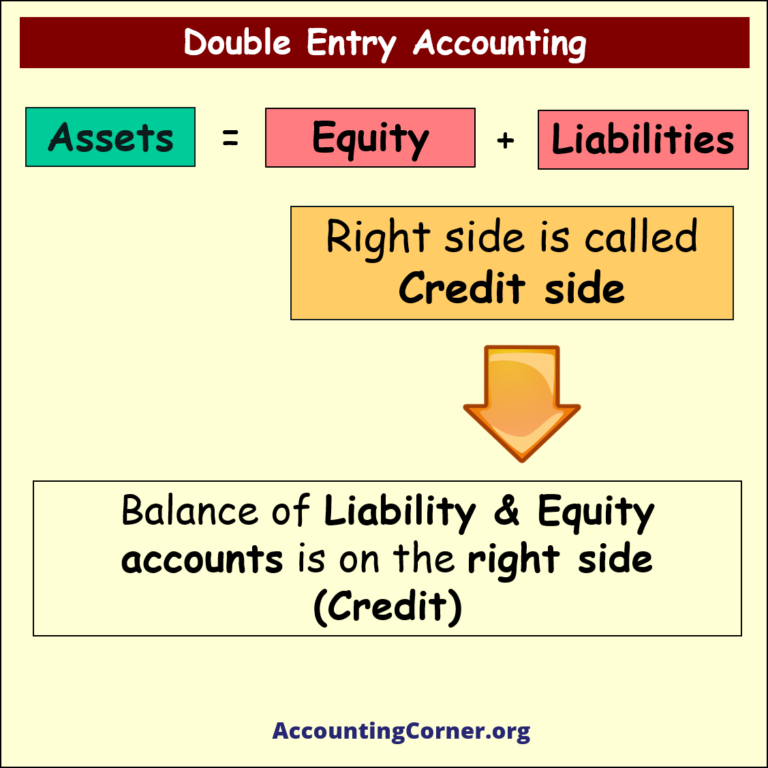
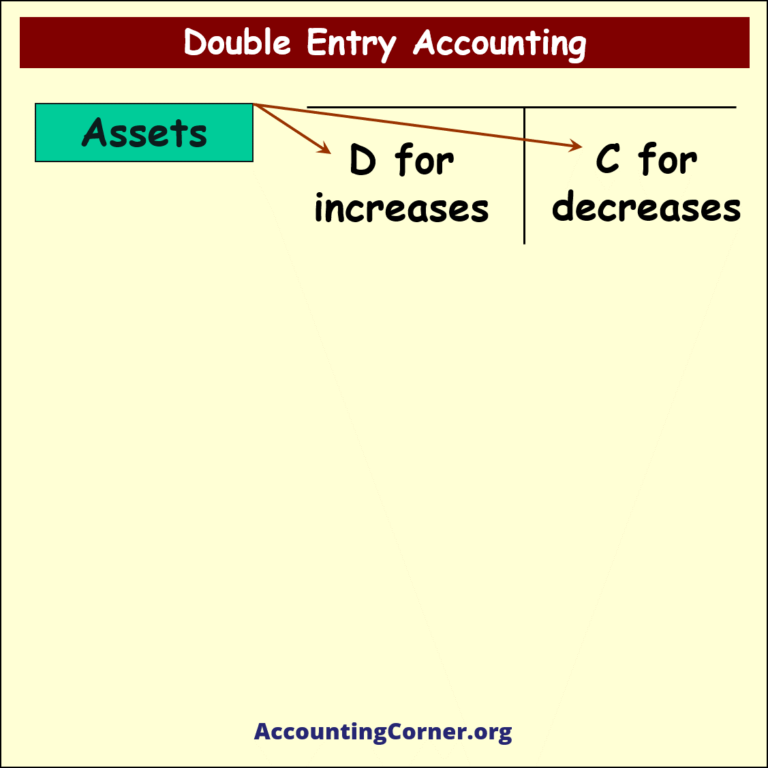
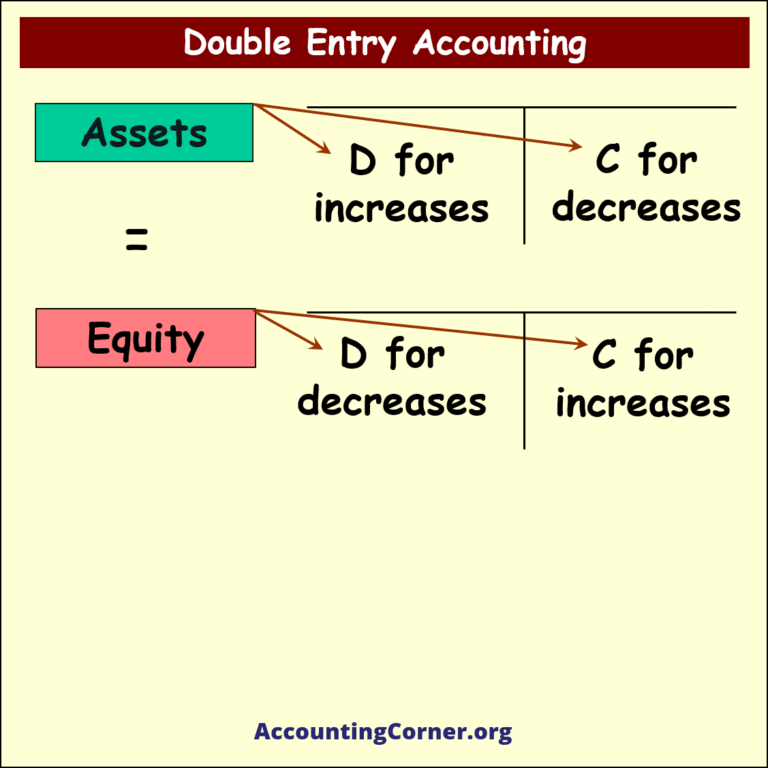
- Double Entry Accounting is a bookkeeping system where every financial transaction has equal and opposite effects in at least two different accounts. It is based on the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. For every debit entry, there is a corresponding credit entry, and vice versa, ensuring the accounting equation remains balanced.
- Importance of Double Entry Accounting:
- This system provides a complete record of financial transactions, making it easier to produce accurate financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
- It enhances the accuracy and reliability of financial information, as each entry is balanced by another, reducing the risk of errors.
- Double Entry Accounting is fundamental for businesses of all sizes as it helps in detailed financial analysis and aids in decision-making.
- Practical Examples:
- For instance, when a business makes a sale on credit, it would record the transaction by debiting accounts receivable and crediting sales revenue. This reflects the increase in assets (receivable) and the increase in equity (revenue).
- If a company purchases equipment, it would debit the equipment account and credit the cash or accounts payable account, reflecting the acquisition of a new asset and the decrease in another asset (cash) or increase in liability (payable).
- Issues and Concerns Related to Double Entry Accounting:
- Complexity: It can be more complex than single-entry accounting, requiring a more in-depth understanding of accounting principles.
- Error Detection and Correction: While the system helps in minimizing errors, detecting and correcting them can be challenging, as it requires tracing back through various accounts.
- Software Dependency: Many businesses rely on accounting software to manage double-entry bookkeeping, which necessitates a dependency on technology and software reliability.
- Training and Expertise Required: Proper implementation of double entry accounting requires trained personnel with a good understanding of accounting principles.
In summary, Double Entry Accounting is a comprehensive and systematic approach to recording financial transactions, which is essential for accurate and reliable financial reporting. It is a cornerstone of modern accounting practices and is crucial for businesses and organizations to maintain a clear and complete financial record.
Double Entry Accounting – Visuals
Double Entry Accounting – Video
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from Double Entry Accounting to AccountingCorner.org home