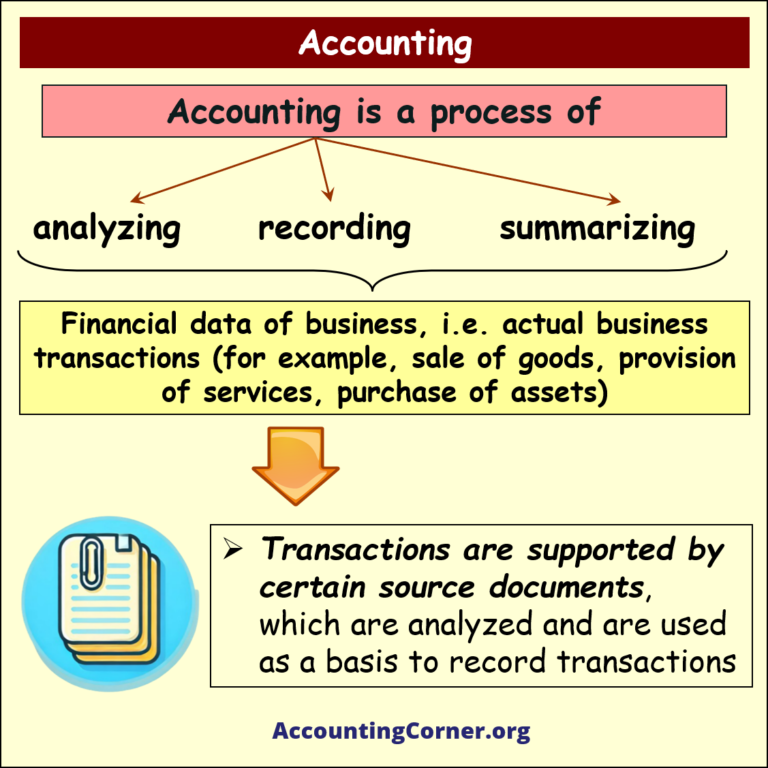
What is Accounting?
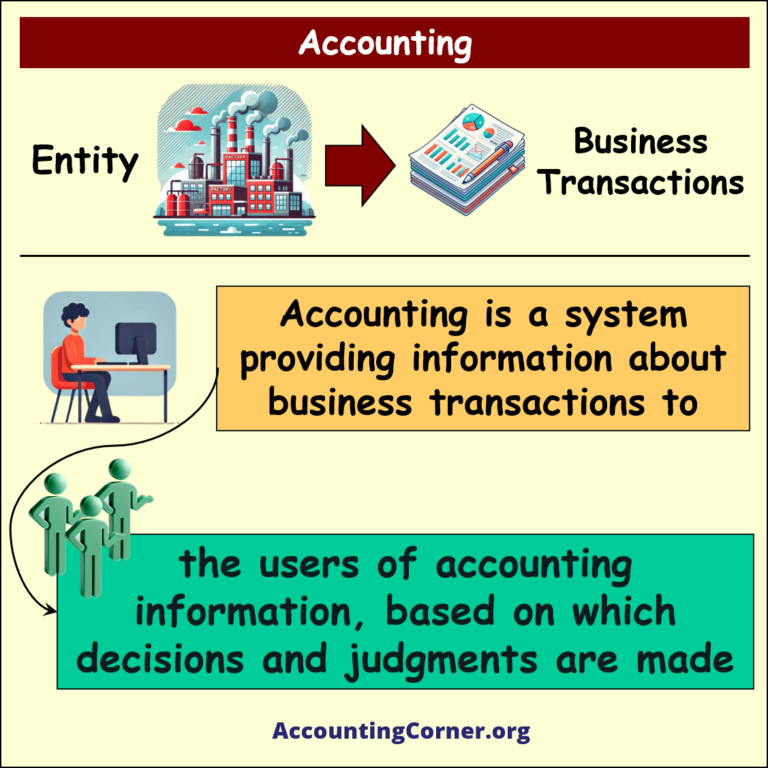
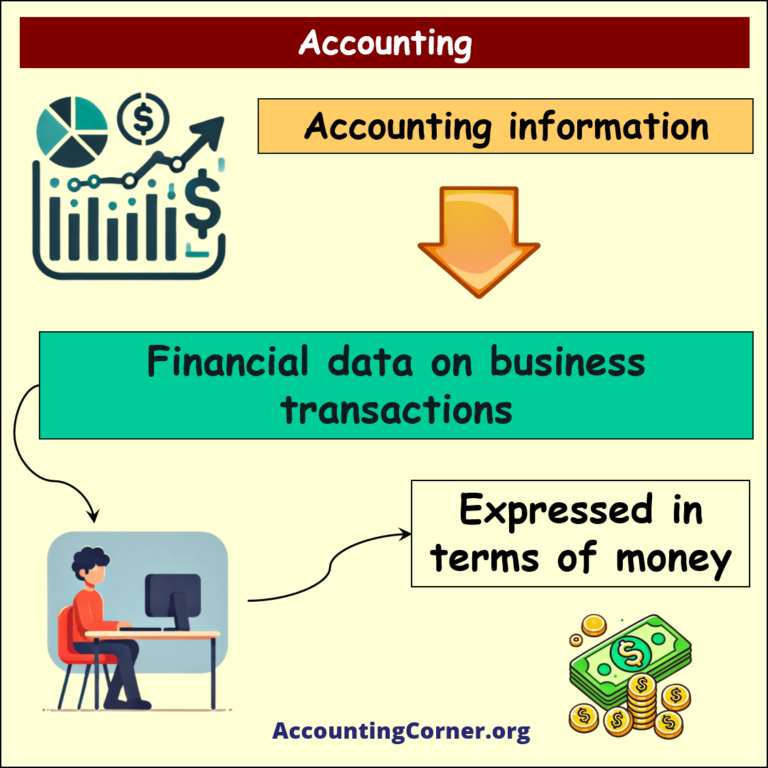
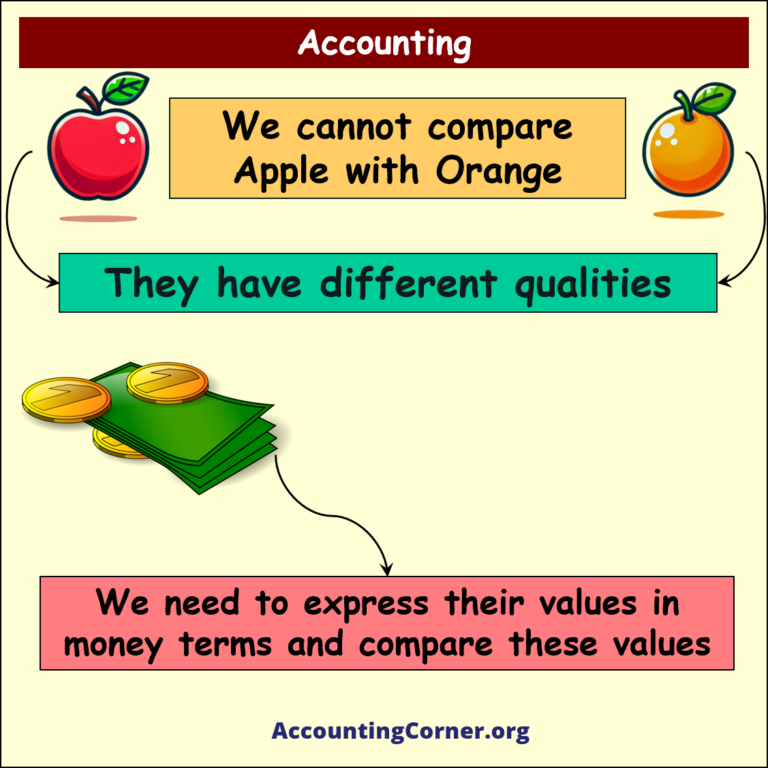
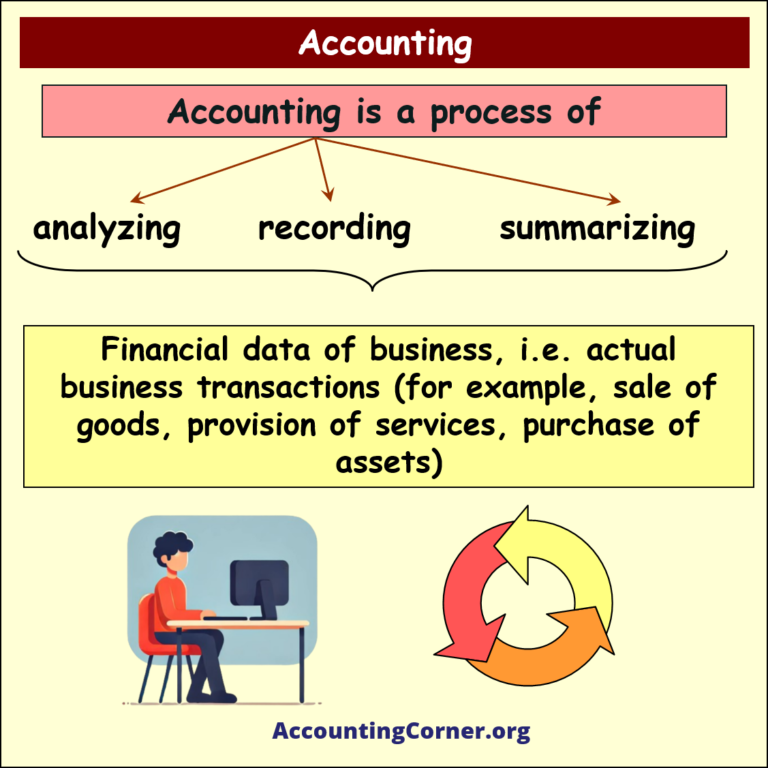
Accounting is the practice of recording, summarizing, analyzing, and interpreting financial transactions. It is often referred to as the “language of business” because it enables stakeholders to understand the financial status and performance of an organization. Accounting involves various tasks like bookkeeping, preparation of financial statements, and auditing. It serves both internal and external audiences, such as management, investors, creditors, and regulators.
Importance of Accounting
- Financial Analysis and Decision-Making: It helps management make informed decisions by providing detailed financial reports.
- Budgeting and Planning: Accounting assists in budget preparation and future planning by analyzing past performances.
- Regulatory Compliance: Accounting helps ensure that businesses comply with laws and regulations by maintaining accurate records and reports.
- Transparency: It ensures transparency in financial reporting, making it easier for investors and stakeholders to understand the company’s financial health.
- Resource Management: Helps in optimizing the use of resources like manpower, material, and machinery.
- Risk Management: Proper accounting helps in identifying risks and threats to the business and allows for timely action.
Types of Accounting
- Financial Accounting: Focuses on the preparation of financial statements for external stakeholders such as investors and creditors.
- Management Accounting: Focuses on generating reports for internal stakeholders, such as managers, to help in decision-making.
- Cost Accounting: Deals with the collection, analysis, and allocation of costs for determining the price of a product or service.
- Tax Accounting: Involves the preparation and filing of tax returns and dealing with issues related to taxation.
- Auditing: An independent examination of accounting records and financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulations.
- Forensic Accounting: Involves investigating financial discrepancies and fraud.
Examples of Accounting
- Balance Sheet: A snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a particular point in time.
- Income Statement: Shows revenue, expenses, and profit or loss over a specific period.
- Cash Flow Statement: Records the flow of cash in and out of a business.
- Budgets: Plans that outline projected income and expenses for a certain period.
- Tax Returns: Documents filed with tax authorities that report income, expenses, and other relevant financial information.
Issues and Limitations of Accounting
- Subjectivity: Certain accounting methods leave room for interpretation, potentially leading to manipulation of figures.
- Complexity: The rules and standards can be very complicated, making it difficult for laypeople to understand the financial statements.
- Historical Nature: Most accounting data is historical and may not be reflective of future performance.
- Non-Financial Factors: Accounting primarily focuses on financial aspects and may overlook qualitative factors like employee morale.
- Regulatory Challenges: Different countries have different accounting standards, which makes it difficult for multinational corporations.
- Cost: The process of accounting, especially for large enterprises, can be expensive.
- Fraud: If the accounting process is not properly overseen, it can lead to fraud and financial disasters, as seen in cases like Enron and WorldCom.
Understanding accounting is crucial for anyone involved in business, as it provides the framework for assessing the financial health and performance of an organization.
What is accounting – visual
What is accounting – video
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from Accounting to AccountingCorner.org home