Find below the Accounting Cycle scheme and Accounting Cycle steps. This is the process, which should be followed in order to account for business transactions properly and provide accounting data to its users for decision making purposes.
 Accounting cycle represents a sequence of certain accounting activities to be followed in a determined order with the purpose to record business transactions and prepare financial statements.
Accounting cycle represents a sequence of certain accounting activities to be followed in a determined order with the purpose to record business transactions and prepare financial statements.
Depending on the accounting period, the activities in this cycle are repeated through each accounting period – month, quarter, year.
Below you will be able to inspect all steps in the accounting cycle separately and understand, what exact actions must be taken under each of them.

Steps of the Accounting Cycle
- Analyze, journalize transactions
- Summarize accounts, general ledger posting
- Trial balance preparation
- Period-end adjusting entries
- Adjusted trial balance preparation
- Preparation of financial statements
- Close general ledger accounts (income/expenses)
Let’s analyse, what accounting procedures are done under each of the above steps in the Accounting Cycle:
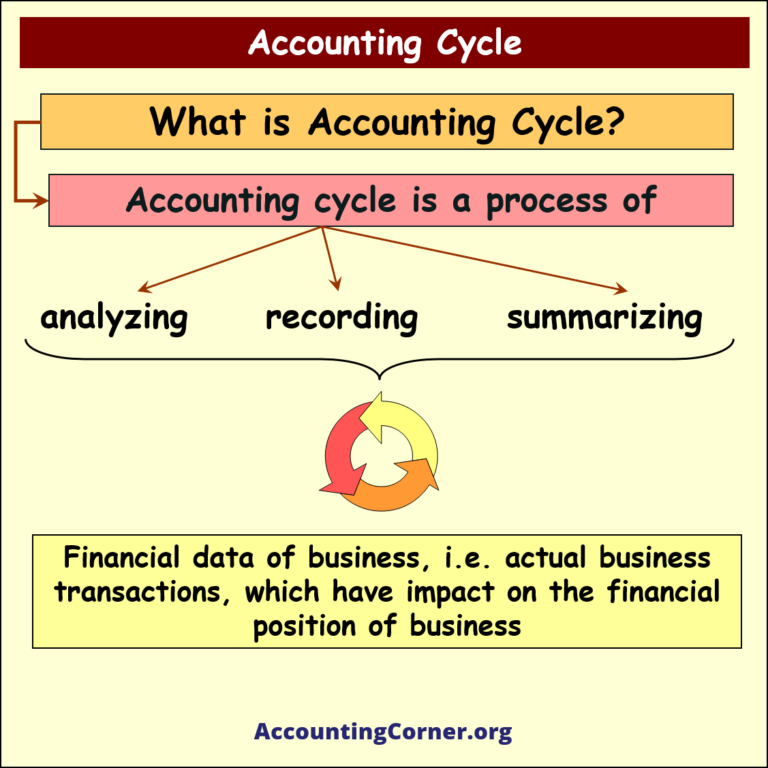
So, what is an accounting cycle?
 Accounting cycle is a process of analyzing, recording, and summarizing financial data of business, which includes actual business transactions, which have impact on the financial position of business
Accounting cycle is a process of analyzing, recording, and summarizing financial data of business, which includes actual business transactions, which have impact on the financial position of business
 Purpose of this process is to prepare financial statements, and have accurate and timely financial data for decision making
Purpose of this process is to prepare financial statements, and have accurate and timely financial data for decision making
![]()
Financial data must provide information on the results of business operations for the period, and information on the structure of assets & their financing sources, which include liabilities and equity, at the end of the period
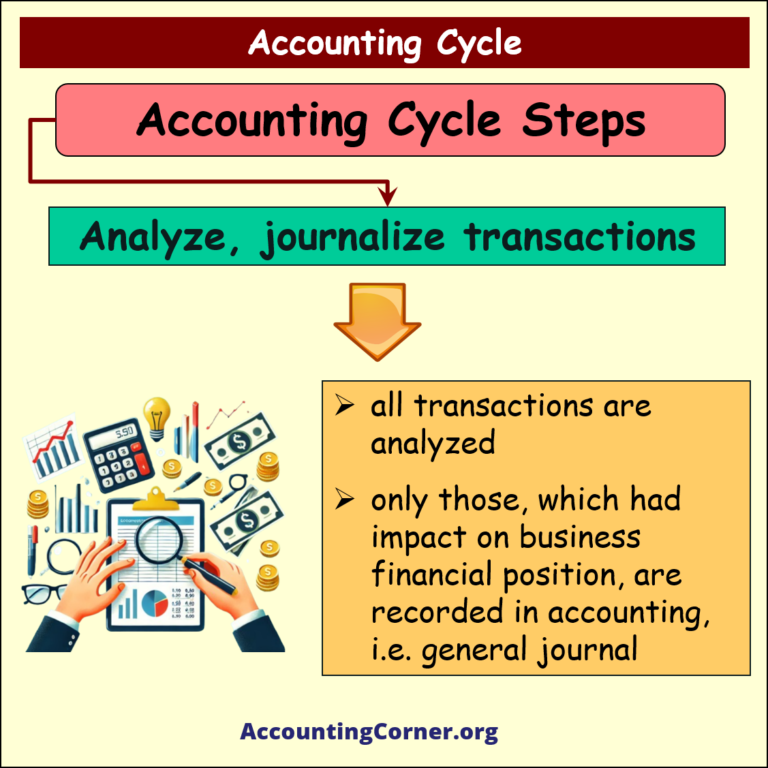
Step 1
 Analyze and journalize transactions
Analyze and journalize transactions
Under this step:
- all transactions are analyzed
- only those, which had impact on business financial position, are recorded in accounting, i.e. general journal
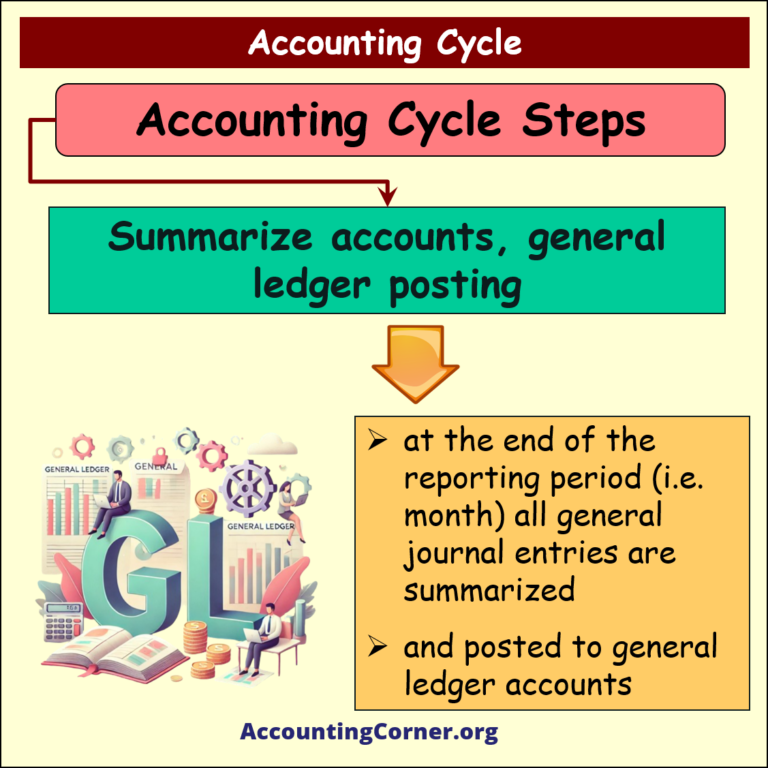
Step 2
 Summarize accounts, perform general ledger posting
Summarize accounts, perform general ledger posting
Under this step:
- at the end of the reporting period (for example, month) all general journal entries are summarized, and
- are posted to general ledger accounts
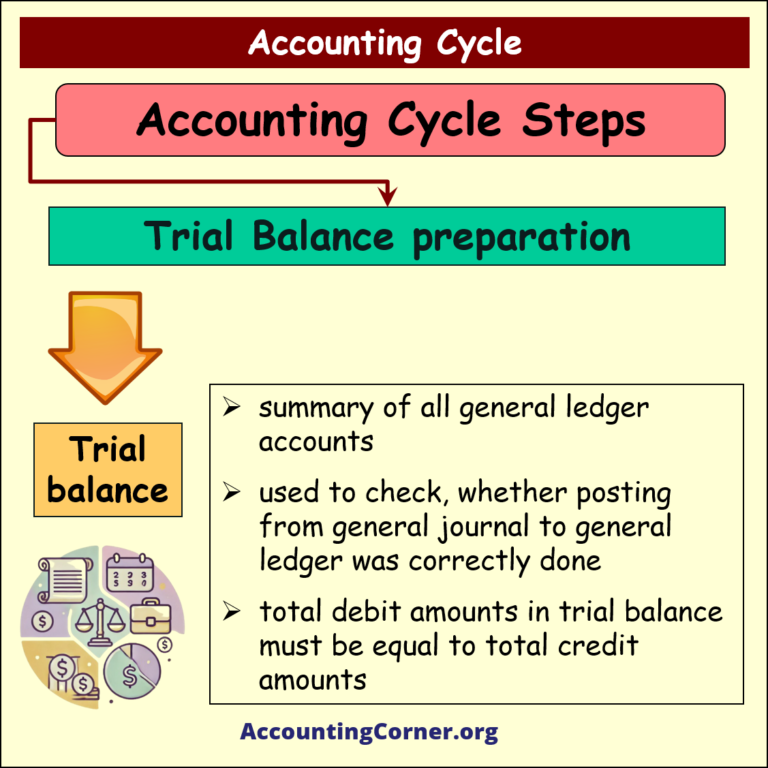
Step 3
 Trial Balance preparation
Trial Balance preparation
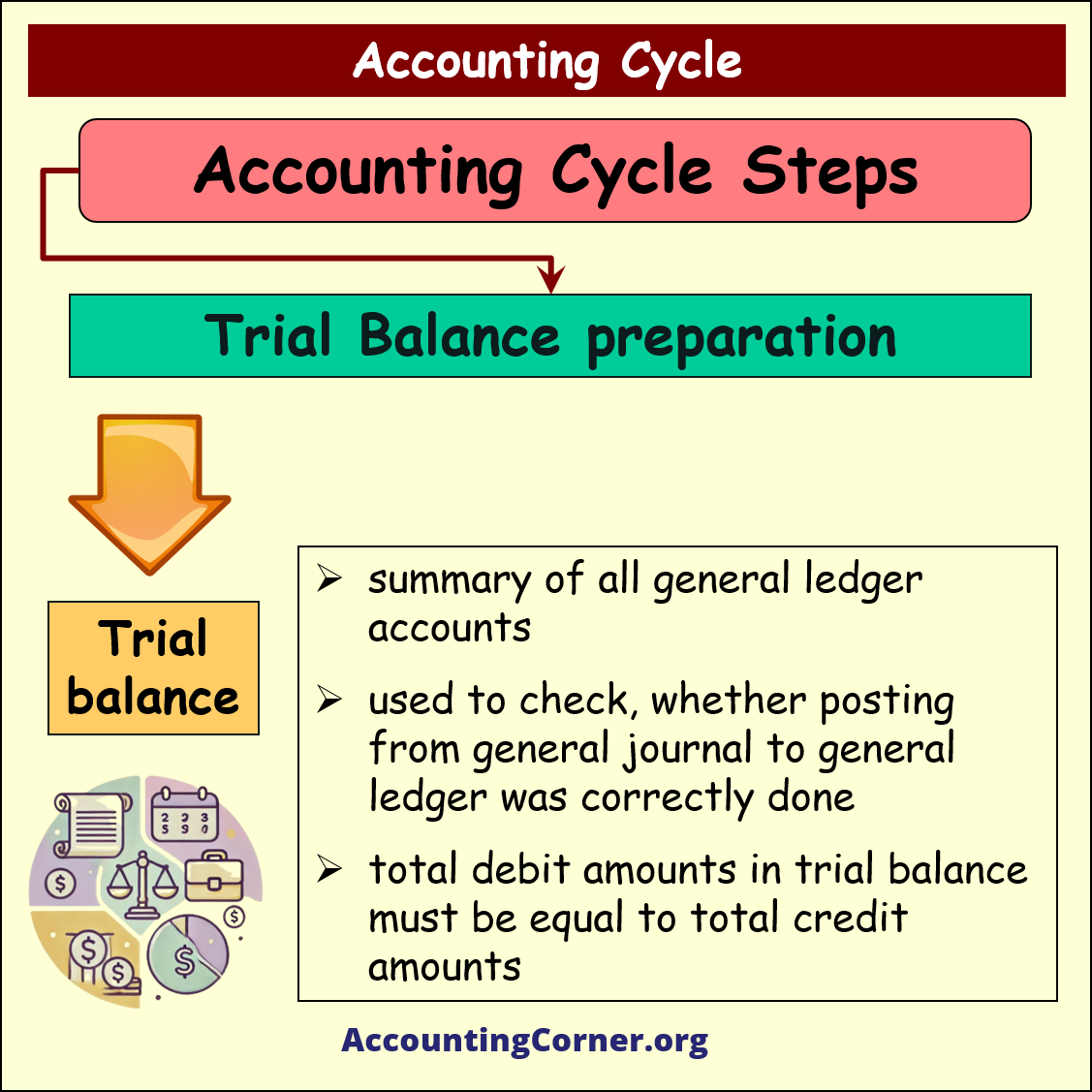
Under this step trial balance is prepared
![]() Trial balance is a summary of all general ledger accounts, used to check, whether posting from general journal to general ledger was correctly done. Total debit amounts in trial balance must be equal to total credit amounts
Trial balance is a summary of all general ledger accounts, used to check, whether posting from general journal to general ledger was correctly done. Total debit amounts in trial balance must be equal to total credit amounts
Step 4
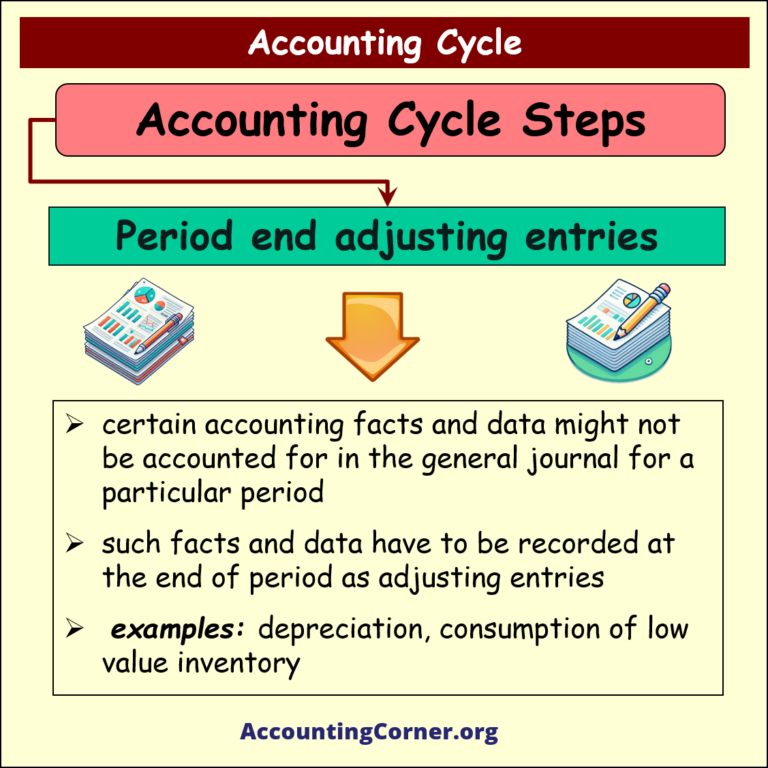
 Recording of Period end adjusting entries
Recording of Period end adjusting entries
Under this step period end ajudsting entries are recorded in the accounting books of the business
- certain accounting facts and data might not be accounted for in the general journal for a particular period
- such facts and data have to be recorded at the end of period as adjusting entries
- examples: depreciation, consumption of low value inventory
Step 5
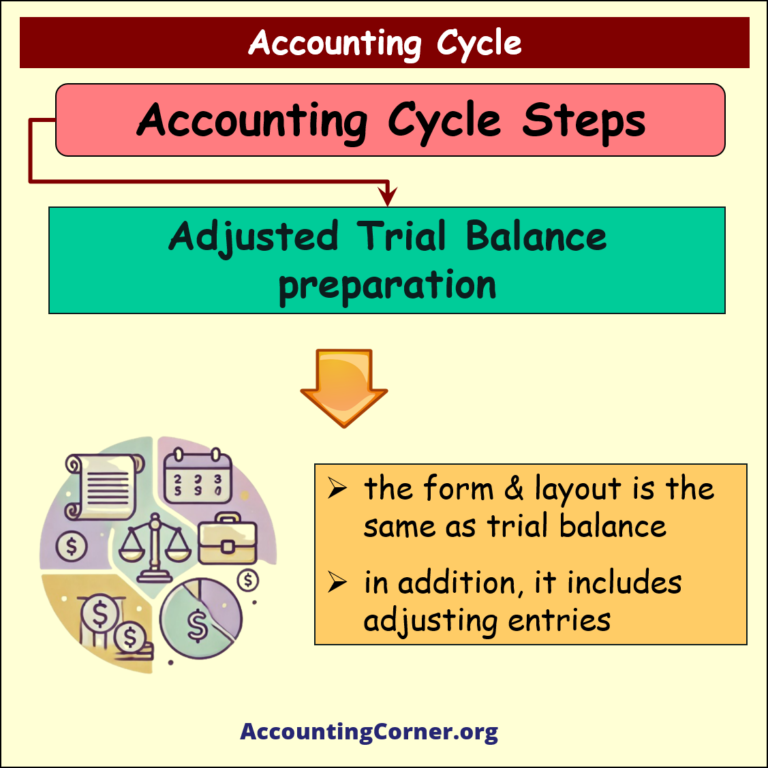
 Adjusted Trial Balance preparation
Adjusted Trial Balance preparation
Under this step adjusted trial balance is prepared
- it has the form & layout, the same as trial balance
- in addition, it includes adjusting entries
Step 6
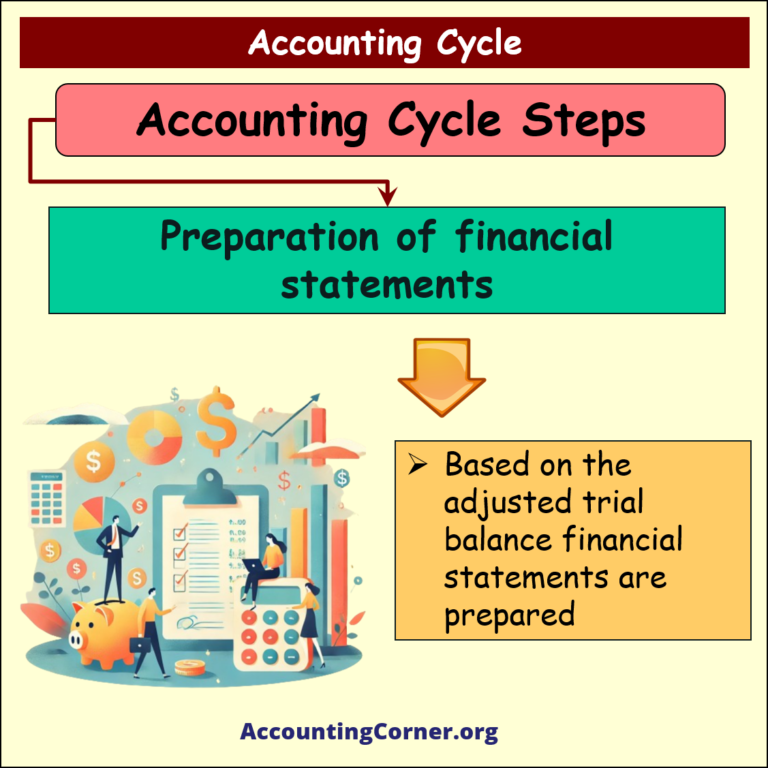
 Preparation of financial statements
Preparation of financial statements
Based on the adjusted trial balance, financial statements are prepared
Step 7
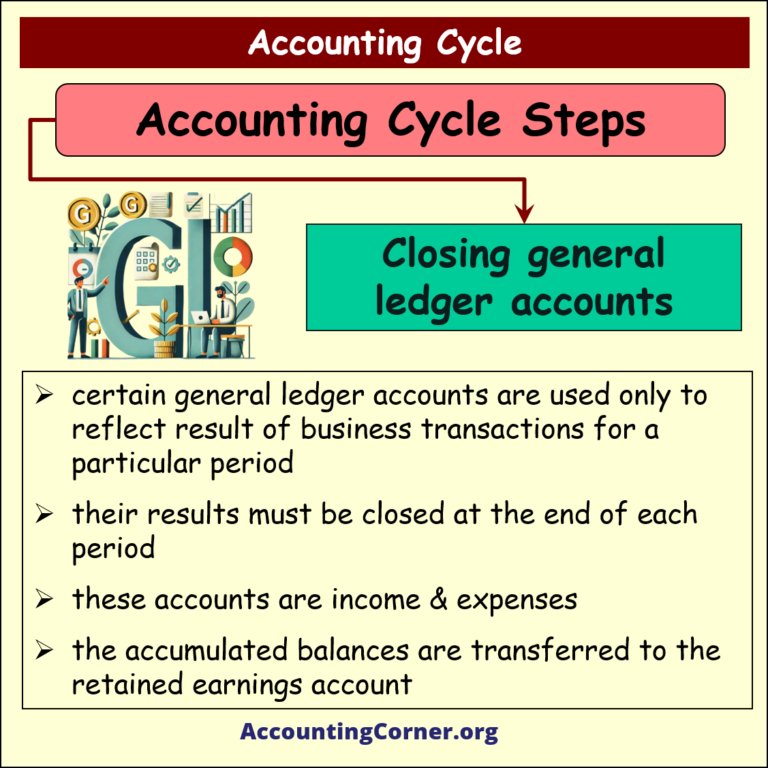
 Closing of general ledger accounts
Closing of general ledger accounts
- certain general ledger accounts are used only to reflect result of business transactions for a particular period
- their results must be closed at the end of each period
- these accounts are income & expenses
- the accumulated balances are transferred to the retained earnings account
We have covered all 7 steps of the accounting cycle
Now you know, what are those steps, and what accounting procedures are performed under each of these steps
So, in the Accounting Cycle the last step is:
 close general ledger accounts, which balances at the end of the accounting period should be zero – Income and Expenses.
close general ledger accounts, which balances at the end of the accounting period should be zero – Income and Expenses.
Accounting Cycle – Financial Accounting Basics – Video
All Visual Material
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from Accounting Cycle to AccountingCorner.org