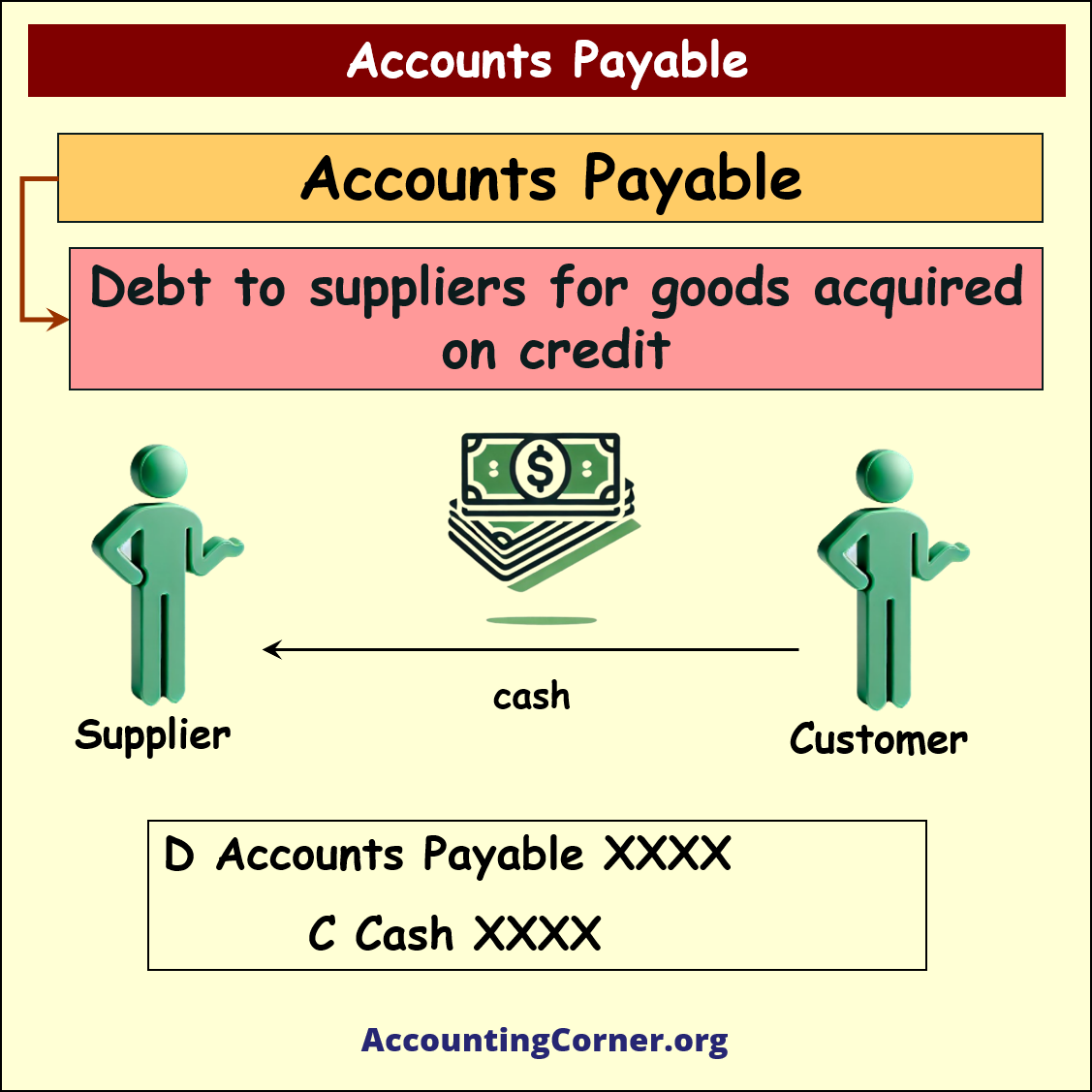
What is accounts payable?
In case a business acquired from the suppliers goods or services, however cash for the acquisition based on the agreement with the supplier will be paid later on after the purchase, the purchaser acknowledges a liability to the supplier.
 Such liability is called Accounts Payable
Such liability is called Accounts Payable
This is a debt of the business to its suppliers for certain acquisitions, like goods or services. Usually when the goods or services are acquired from the suppliers and the payment is postponed till the certain date, we call it “acquisition on credit”.
On the Balance Sheet this item is reflected on the Liabilities & Equity side under Liabilities caption. Usually they have their due date, i.e. the date till which the debt should be paid back. Sometimes suppliers provide certain discounts in case the debt is covered earlier before the due date.
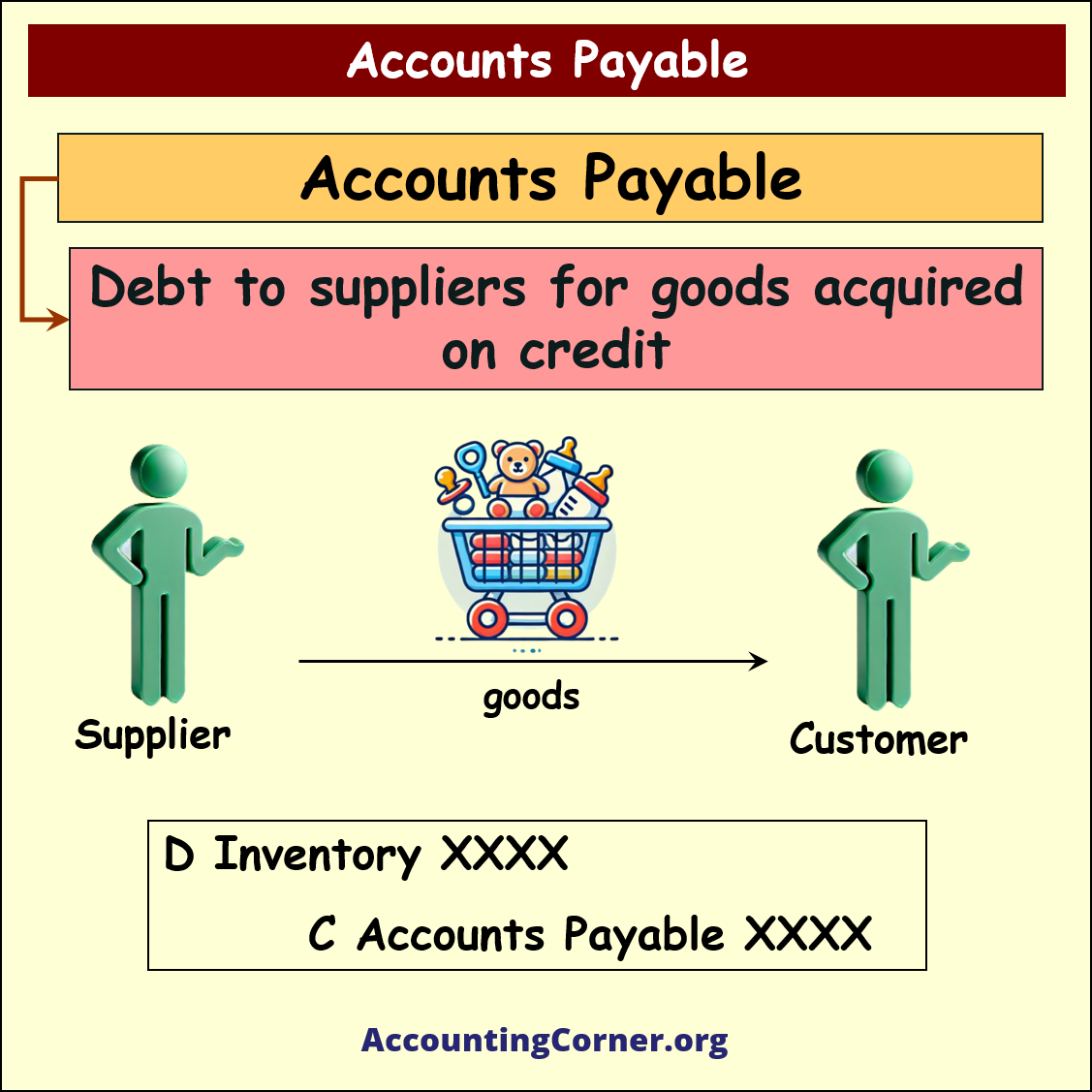
As accounts payable represent debt to suppliers for goods acquired on credit or services acquired on credit, when a customer purchases goods from the supplier the following accounting entries are done:
- Debit entry to Inventory if inventory was acquired. Alternatively another type of assets is debited depending on what assets were acquired (examples can be plant assets, office stationary or low value inventory)
- Accounts payable are Credited, increasing business liability to the supplier of the items, which were purchased on credit
D Inventory (other asset)
C Accounts Payable
After the payment is done to the supplier, the following accounting entry is done:
D Accounts Payable
C Cash
Practical Examples
First question of course what accounting entries have to be made when accounting for the this item of balance sheet. Let assume that on October 10, 2009 the company HCC acquired goods from its supplier for $1500 on credit, payment for which will have to be made till November 10, 2009. To account for the acquisition we made the following entry:
- D Inventory $1500
- ___C Accounts Payable $1500
When till November 10, 2009 the payment is made, the following entry will be recorded:
- D Accounts Payable $1500
- ___C Cash $1500
Since this balance sheet item account is a liability account, all the increase in this account are reflected on the credit side, all the decrease – on the debit side. The account will have credit closing balance.
Discounts on early payments
In certain cases based on the agreement with the supplier, suppliers can provide discounts if payment is executed earlier. In such way suppliers encourage faster payment for the suppliers made. Such discounts are called Discounts for Early Payments

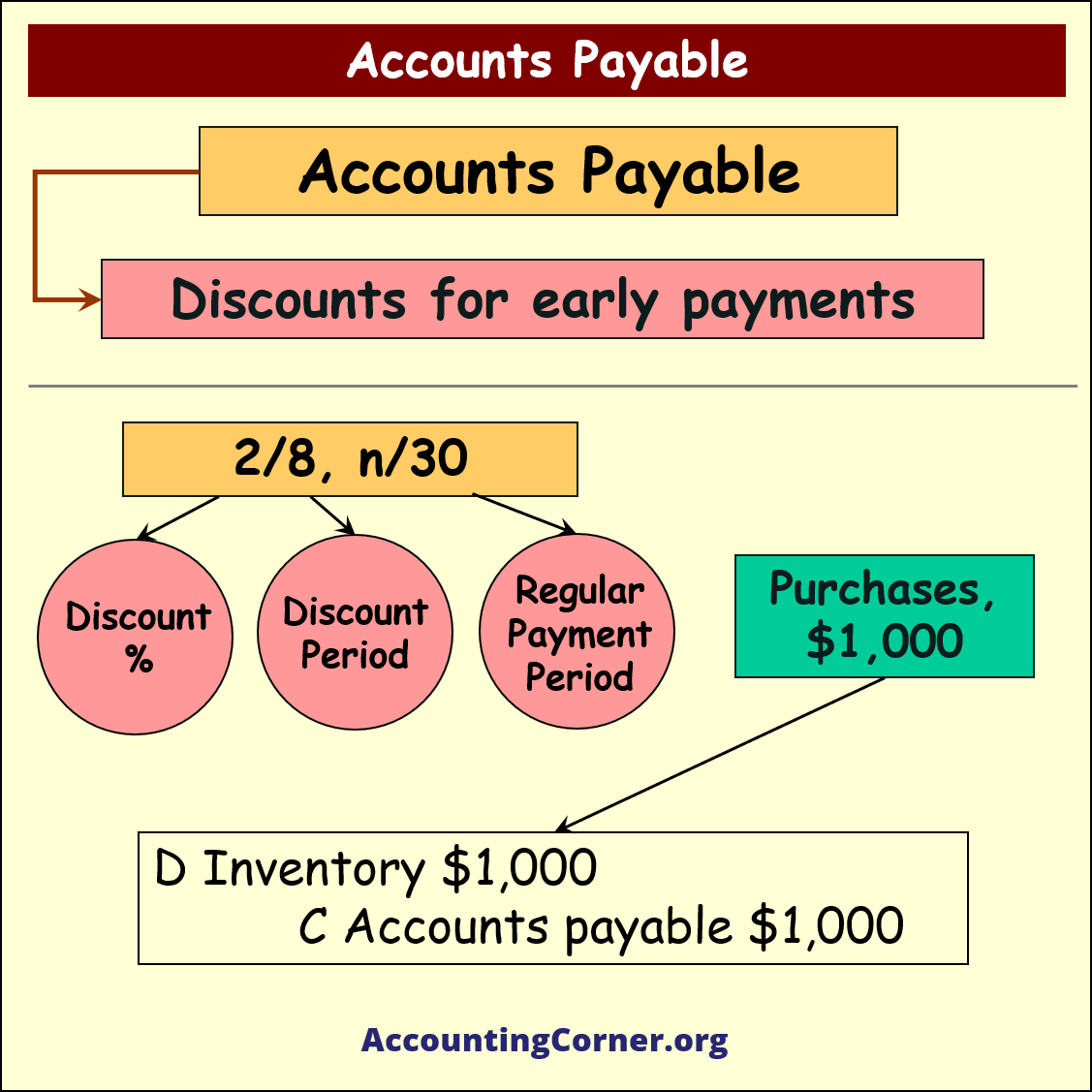
For example, if the supplier sets the following conditions for the payment:
 2/10 and n/30
2/10 and n/30
This means, that general payment terms for the supplies is 30 days, i.e. n/30
2 is discount % and 10 is discount period, i.e. if payment is done withing 10 days supplier will give 2% of discount on the value of payment.
For example, let’s assume that the purchase on credit amount was $1,000, with the following payment conditions: 2/8 n/30. The following accounting entry is done on the time of the purchase:
- D Inventory $1,000
- ____C Accounts Payable $1,000
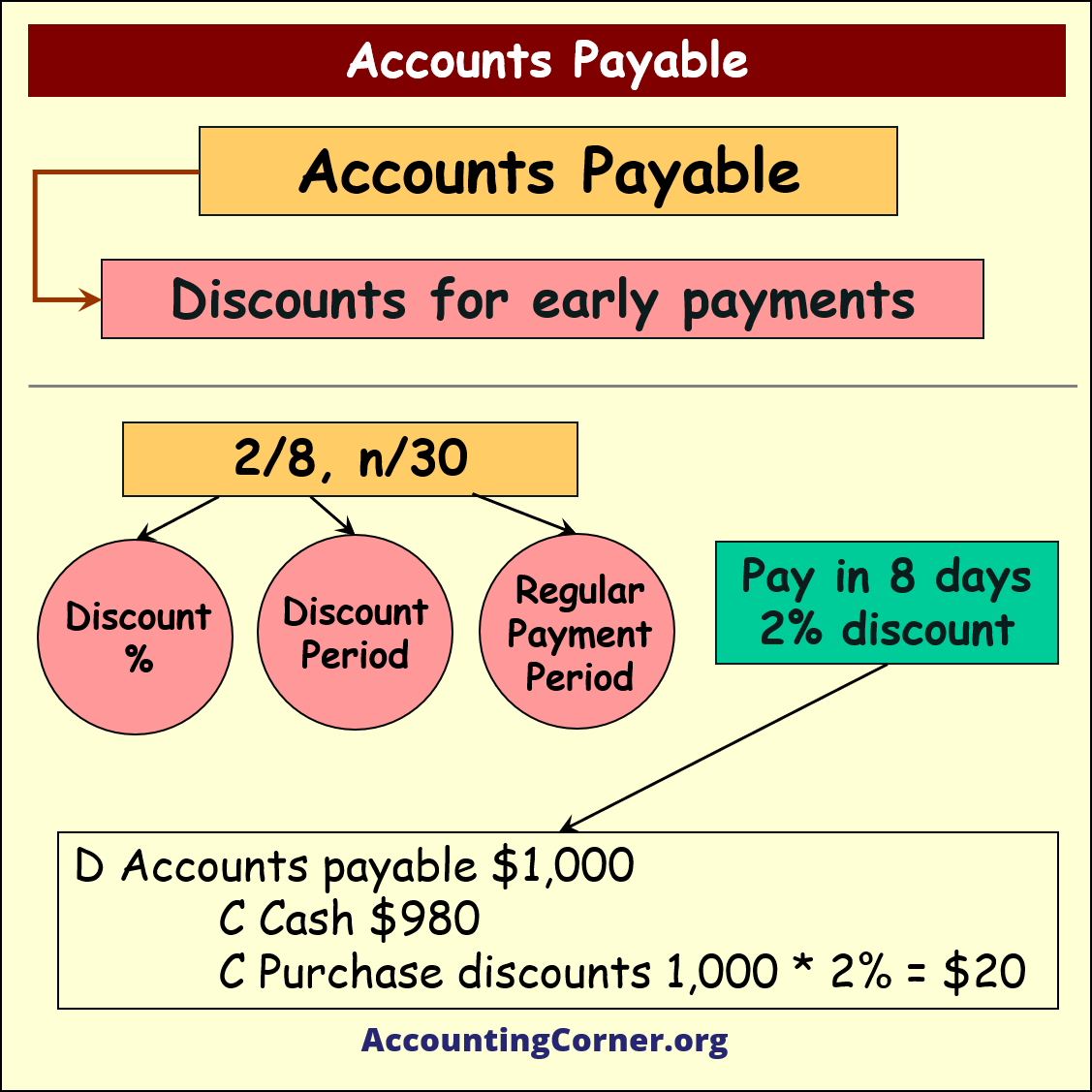
Such entry indicates the business has a liability of $1,000 to the supplier of inventory. If the payment is executed in 8 days, supplier will provide 2% discount on the amount of payment.
In case of earlier payment the following entry is done:
- D Accounts Payable $1,000
- ____C Cash $980
- ____C Purchase discounts 1,000*2%=$20
 2% discount on early payment amounting to $20 decreases amount of payment, i.e. less cash is spent
2% discount on early payment amounting to $20 decreases amount of payment, i.e. less cash is spent
In case the payment is done withing standard period period, i.e. 30 days, no discount is provided by the supplier. The following accounting is done:
- D Accounts Payable $1,000
- ____C Cash $1,000

Accounts Payable – Video
Visual Presentation
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from Accounts Payable to AccountingCorner.org