Here we will come back to the concept of Balance Sheet and provide explanations on what items you can find on this financial statement and also present Balance Sheet Example for a better understanding, how to compose it and what information is necessary for its preparation.
Here there will be also balance sheet template and sample format presented and explained to guide you through the process and provide knowledge of how to prepare this financial statement and understand it.
The Essence Of Balance Sheet
Coming back to the essence of Balance Sheet remember that it is one of the three main financial statements, which include:
 Balance Sheet reflects structure of the company’s assets and financing sources, used to finance these assets (i.e. equity and/or liabilities) as of particular date
Balance Sheet reflects structure of the company’s assets and financing sources, used to finance these assets (i.e. equity and/or liabilities) as of particular date
This means, that in this financial statement we can find information on what kind of assets business had on the particular day and how these assets were financed, i.e.:
- either by the own means of shareholders (equity), or
- by the borrowed financial means (liabilities), or by the mix of these two sources
From the name of this financial statement, i.e. Balance Sheet, we can understand, that there should be a balance between its parts, i.e.
This is true since this financial statement reflects the essence of the Accounting Equation.
Items On The Balance Sheet
The following items can be found on the Balance Sheet and will be included into the sample Balance Sheet:
 I. Assets – these are physical (tangible) things or intangible items which have a monetary value and are owned by the business. On the Balance Sheet assets are divided into:
I. Assets – these are physical (tangible) things or intangible items which have a monetary value and are owned by the business. On the Balance Sheet assets are divided into:
a) current assets – which are reasonably expected to be realized in cash or sold within one year or less in the normal operations of the business;
b) long-term (fixed) assets – permanent assets or relatively fixed in nature and used by the business in its operations for the period longer than one year.
 II. Equity (Owners’ equity) – residual claim against total assets of business after all the liabilities are deducted. In other words equity represents right of the shareholders to get share of the assets the business owns after all liabilities have been paid. Equity is not classified into current and long-term part, since it does not have maturity date and there is no obligation to pay back equity to the shareholders. It might be done only after the liquidation of the business.
II. Equity (Owners’ equity) – residual claim against total assets of business after all the liabilities are deducted. In other words equity represents right of the shareholders to get share of the assets the business owns after all liabilities have been paid. Equity is not classified into current and long-term part, since it does not have maturity date and there is no obligation to pay back equity to the shareholders. It might be done only after the liquidation of the business.
 III. Liabilities – debts owed to third parties, i.e. creditors, which have a certain maturity date and must be repaid.
III. Liabilities – debts owed to third parties, i.e. creditors, which have a certain maturity date and must be repaid.
Liabilities are also divided into 2 groups:
a) current liabilities – payable within the period of one year or shorter. Usually to be repaid back from the current assets
b) long-term liabilities – payable within the period longer than one year
Balance Sheet Example
Below you can find Balance Sheet Example and related explanations on the presentation of separate items in this financial statement.
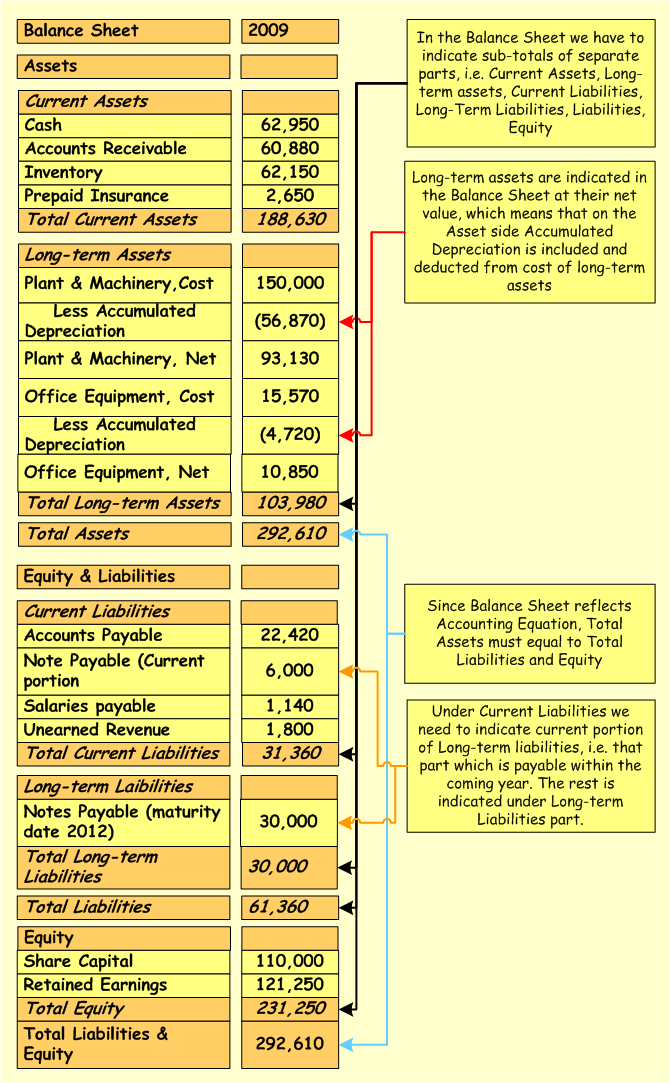
Additional comments on the Sample Balance Sheet (check also more examples on balance sheet accounts):
- Items in the Balance Sheet (explore Balance Sheet Definition here) on the Assets side are presented starting from the most liquid ones and ending with the least liquid. Liquidity means the speed with which assets can be converted into cash. We start from Cash, then go to the Accounts Receivable, which can be quite quickly converted into cash, then to Inventories, which are less liquid comparing to the Accounts Receivable and so on
- In the Balance Sheet on the Liabilities and Equity side first we include liabilities, i.e. showing how much financing the business will have to return to creditors, and then include equity, i.e. residual right of shareholders to get assets, which remain after all liabilities are paid.
- This is a Sample Balance Sheet, not a template, which can be used for any business. In practice depending of the types of activities the business carries on the Balance Sheet might include more items than indicated above
One More Balance Sheet Sample
Find here simplified Balance Sheet Sample. This is a snapshot of a fictional company’s financial position as of December 31, 2022. All figures are in thousands of dollars.
Balance Sheet As of December 31, 2022
| Assets | Amount ($) | Liabilities | Amount ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Assets | Current Liabilities | ||
| Cash | 10,000 | Accounts Payable | 5,000 |
| Accounts Receivable | 8,000 | Salaries Payable | 1,000 |
| Inventory | 7,000 | Short-term Loans | 2,000 |
| Prepaid Expenses | 1,000 | Taxes Payable | 500 |
| Total Current Assets | 26,000 | Total Current Liabilities | 8,500 |
| Non-Current Assets | Non-Current Liabilities | ||
| Property, Plant, & Equipment | 20,000 | Long-term Loans | 5,000 |
| Intangible Assets | 4,000 | Deferred Tax Liabilities | 1,000 |
| Investments | 6,000 | ||
| Total Non-Current Assets | 30,000 | Total Non-Current Liabilities | 6,000 |
| Total Assets | 56,000 | Total Liabilities | 14,500 |
| Equity | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Common Stock | 30,000 |
| Retained Earnings | 11,500 |
| Total Equity | 41,500 |
| Total Liabilities & Equity | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Total Liabilities + Total Equity | 56,000 |
This balance sheet is balanced, meaning that Total Assets = Total Liabilities + Total Equity. Note that this is a simplified example and actual balance sheets may contain more line items and details.
All Balance Sheet Related Topics to Explore:
- Balance Sheet – What is a Balance Sheet?
- Balance Sheet Accounts
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement Vs Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Equation
- Balance Sheet Formula
- Balance Sheet Format
- How to Read Balance Sheet?
- Personal Balance Sheet
- Common Size Balance Sheet
- Trial Balance Sheet
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from Balance Sheet Example to AccountingCorner.org