In the complex world of business management, understanding the nuances of workforce planning and budget allocation is crucial. One concept that stands at the forefront of this challenge is the Full-Time Equivalent (FTE). This article aims to demystify FTE, showinf what does FTE stand for, highlighting its definition, types, importance, issues, and practical applications.
What is FTE?
So what does FTE mean? FTE is a calculation used to convert the hours worked by part-time employees into a comprehensive standard for full-time employees. This metric is essential in various aspects of business, from accounting to human resources management, enabling organizations to quantify and analyze their workforce in a standardized way.

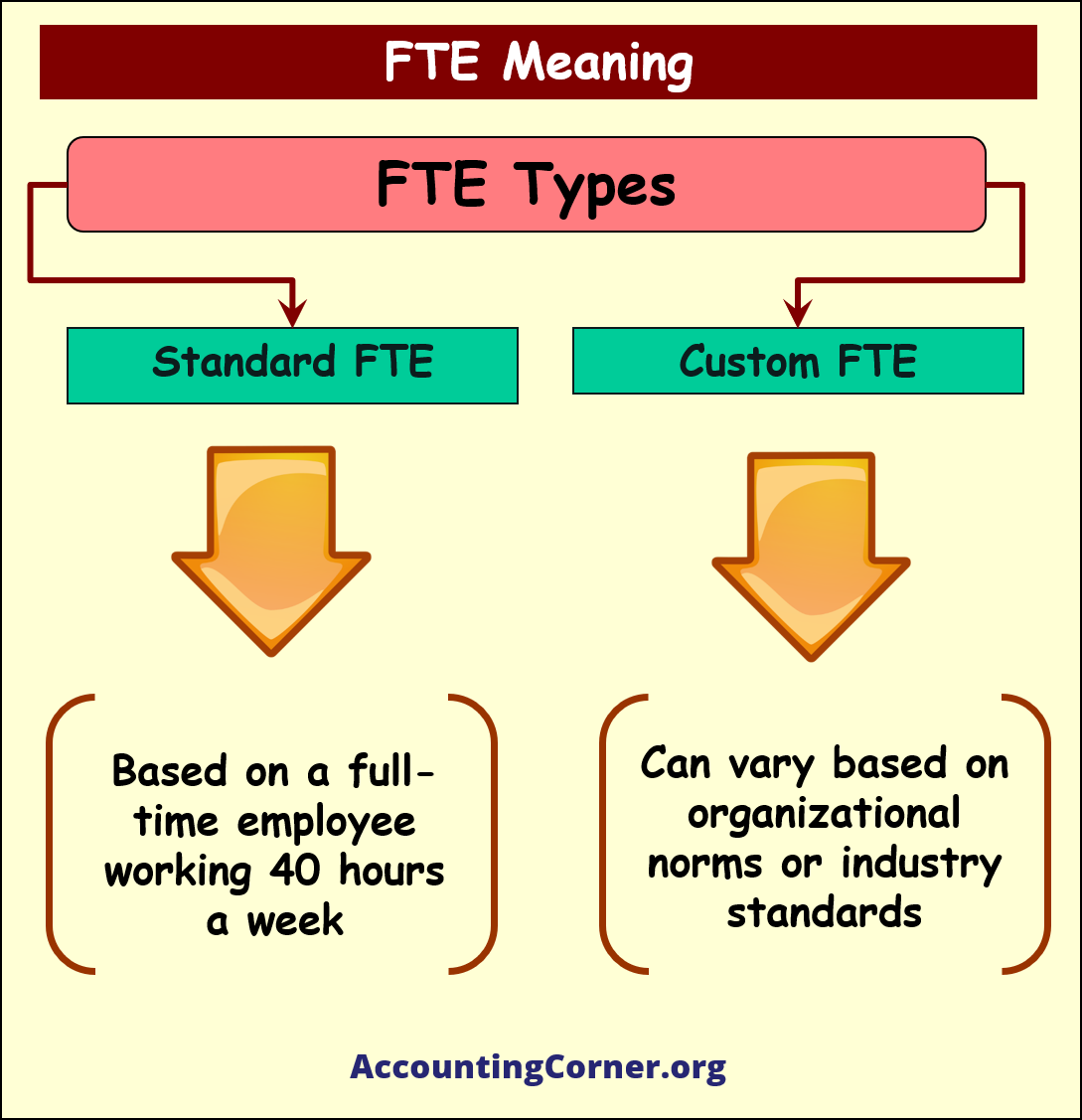
Types of FTE
- Standard FTE: This is the most common type, usually based on a full-time employee working 40 hours a week.
- Custom FTE: Custom FTE models are adapted according to organizational needs or industry standards, allowing for flexibility in defining what constitutes a full-time workload.
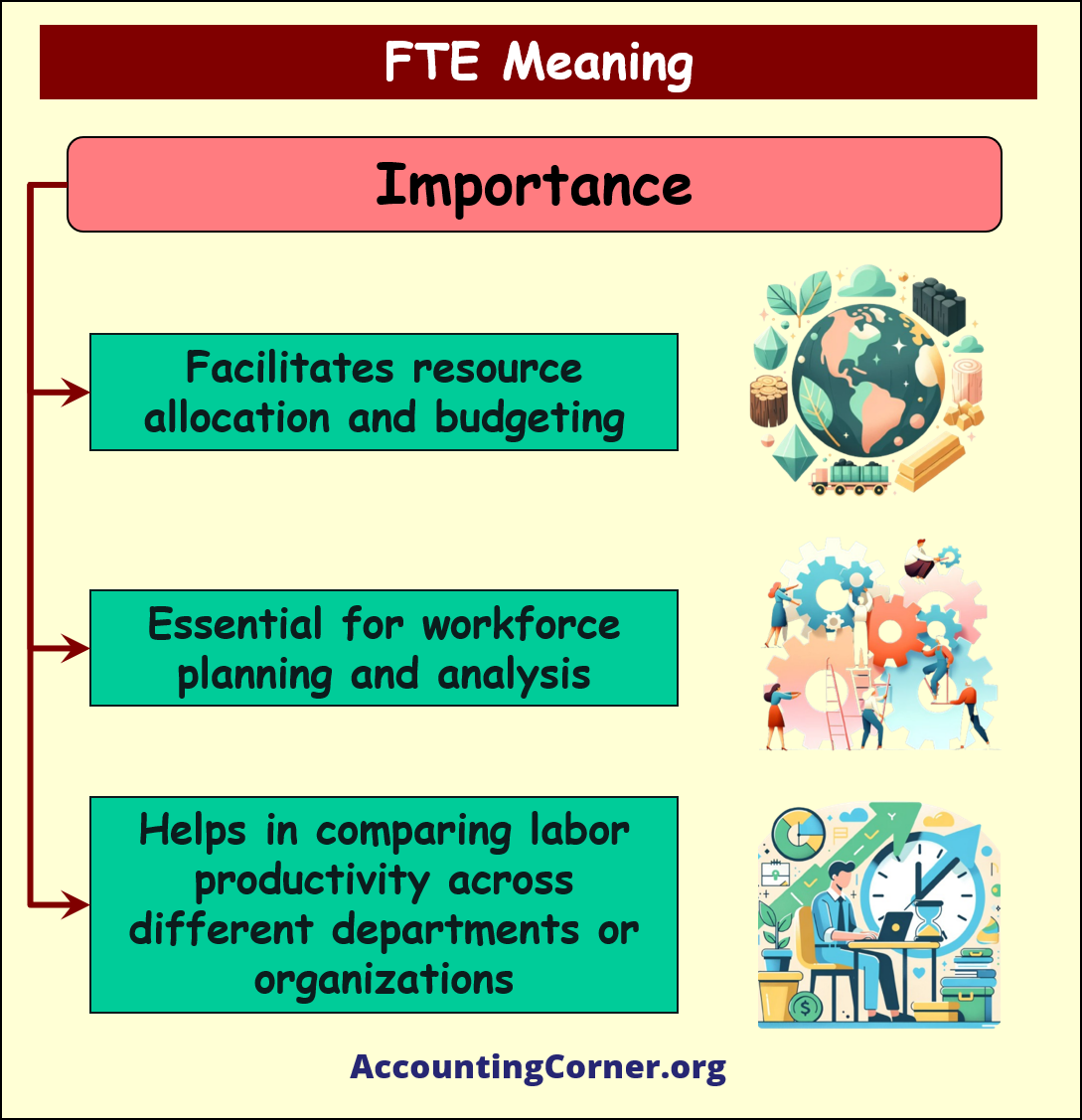
Importance of FTE
- Resource Allocation and Budgeting: FTE plays a pivotal role in determining how resources are allocated and budgets are set, ensuring efficient use of both.
- Workforce Planning and Analysis: It helps in the strategic planning of workforce requirements, considering both part-time and full-time needs.
- Labor Productivity Comparison: FTE is a valuable tool for comparing labor productivity across different departments or organizations, offering insights into workforce efficiency.
Formula on FTE
The most common formula to calculate FTE is:
“Full-Time Hours” is generally the number of hours considered to be full-time in a given time period (often 40 hours per week in the United States).
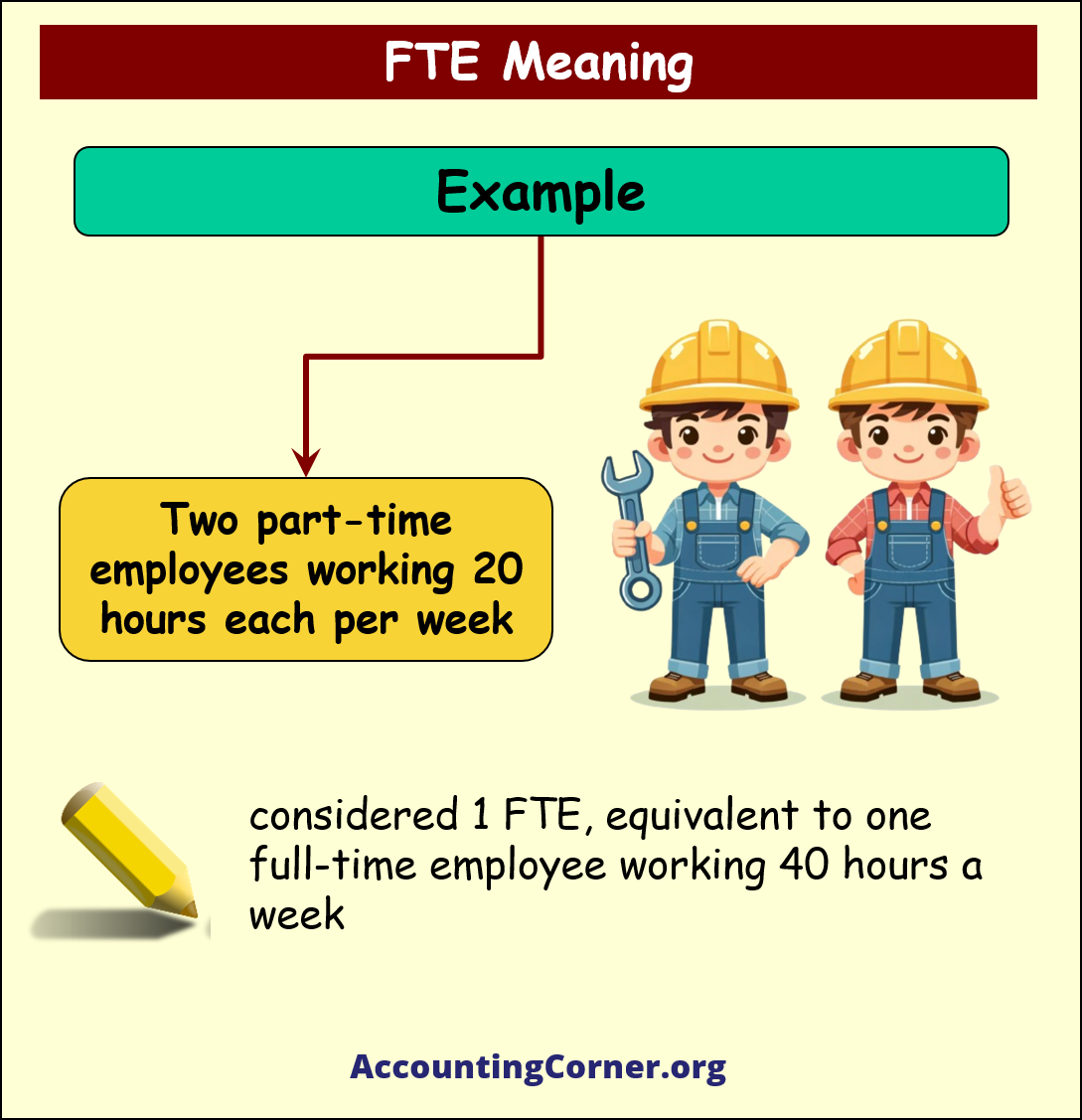
Examples of FTE
- Consider two part-time employees, each working 20 hours per week: combined, they represent 1 FTE. This is equivalent to one full-time employee working a standard 40-hour week. This example illustrates how FTE simplifies understanding part-time work contributions in terms of full-time work.
- Employee FTE: If a company has 10 full-time employees and 5 part-time employees who each work 20 hours per week, the FTE would be 10+(5×20/40)=10+2.5=12.5.
- Student FTE: If a school has 200 full-time students and 50 part-time students who attend half the number of courses as full-time students, the FTE student count would be 200+(50×0.5)=200+25=225.
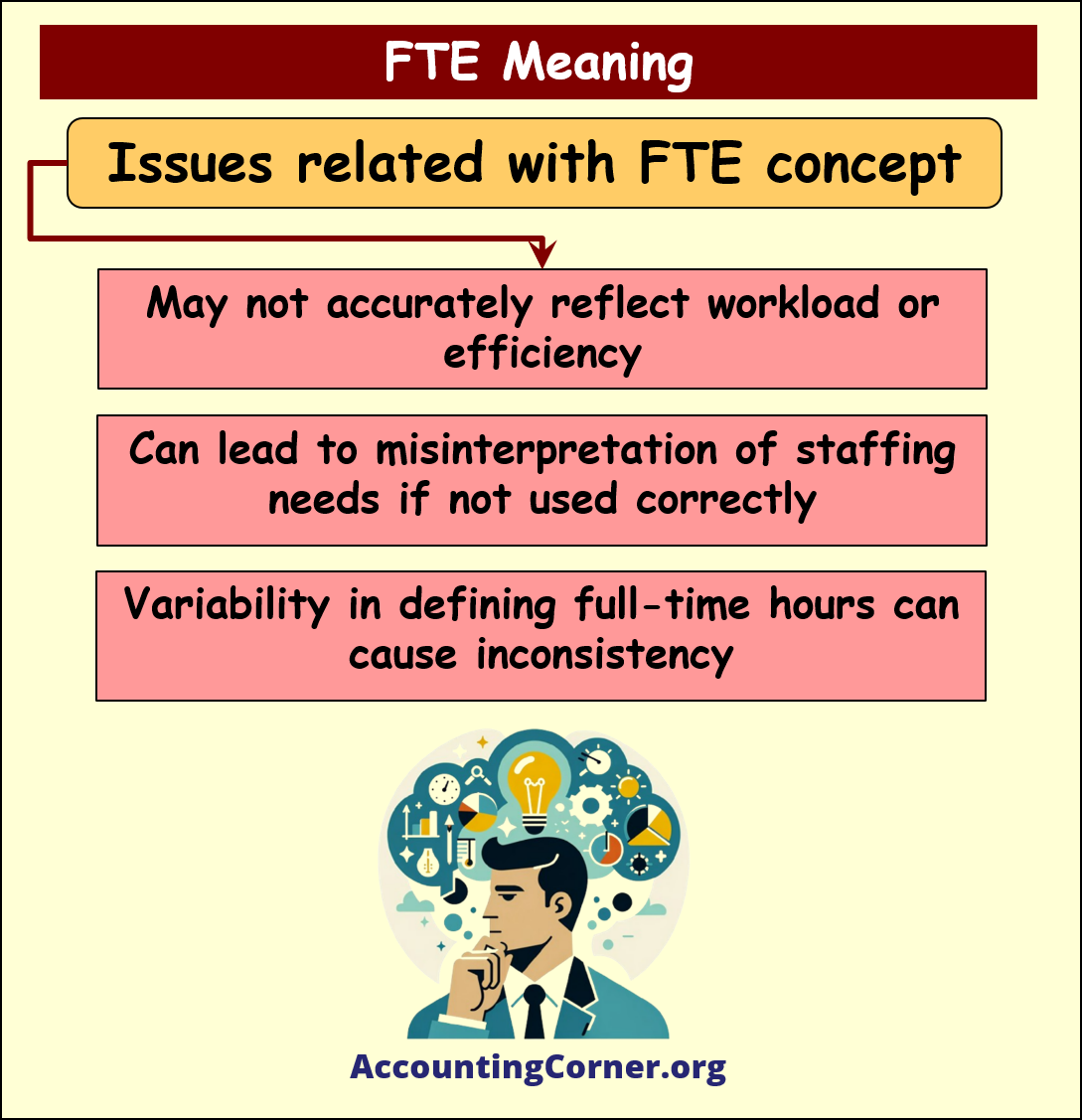
Issues and Limitations of FTE
- Workload and Efficiency Reflection: Sometimes, FTE may not accurately reflect the actual workload or efficiency of employees.
- Staffing Needs Misinterpretation: Incorrect application of FTE can lead to misinterpretation of staffing requirements.
- Inconsistency: Variability in defining full-time hours across different organizations or industries can lead to inconsistency in FTE calculations.
Conclusion
The Full-Time Equivalent is a vital tool in the arsenal of business management. Understanding and correctly applying the concept of FTE can lead to more informed decision-making in resource allocation, workforce planning, and productivity analysis. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to the world of business, grasping the concept of FTE is essential for navigating the modern workforce landscape.
FTE Meaning – Visual Material
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from FTE Meaning to AccountingCorner.org home