What is an income statement?
Income Statement, which also can be called Profit and Loss Statement, is one of the main financial statements that shows the following information about a particular business:
- revenues
- expenses (different types of expenses)
- profit or loss
Income Statement is prepared for a particular period of time. The purpose of an income statement is providing an overview of the business financial performance for the reporting period, which can be month, quarter, year.
 Income statement is an important financial report, which is used to evaluate business financial performance over a certain period of time. It provides information about a company’s ability to generate revenue, manage expenses and earn profit. This financial statement can be used by investors, creditors, other users, who are making decisions related to the business based on information provided in this financial statement, evaluating business financial performance for a certain period of time.
Income statement is an important financial report, which is used to evaluate business financial performance over a certain period of time. It provides information about a company’s ability to generate revenue, manage expenses and earn profit. This financial statement can be used by investors, creditors, other users, who are making decisions related to the business based on information provided in this financial statement, evaluating business financial performance for a certain period of time.
While preparing Income Statement or analyzing sample Income Statement it is important to remember matching principle, i.e. revenue in the Income Statement is recognized at the moment the sale occurs despite the fact that cash is not received yet.
Expenses recognized in the Income Statement are only those which relate to the revenue earned for the period, i.e. they are matched against the revenue.
Income statement definition
Income Statement, which also can be named Profit and Loss Statement ( abbreviation: P&L), is one of the main financial statements, which reports revenues, expenses, profit and loss of a particular business for a certain period of time. This period of time is called reporting period.
Income statement is one of the three main financial statements, including Balance Sheet and Cash Flows Statement, and is used to assess business financial performance and profitability.
 First item on the Income statement is revenue or sales. This is the total amount of money earned by the business from the sale of goods or provision of services over a particular period of time.
First item on the Income statement is revenue or sales. This is the total amount of money earned by the business from the sale of goods or provision of services over a particular period of time.
 Further on cost of goods sold (COGS) or cost of sales are deducted from revenue. Cost of goods sold or Cost of Sales usually includes direct costs of producing goods, which were sold during the period of time in question, or cost of delivering the services incurred during the reporting period to provide these services.
Further on cost of goods sold (COGS) or cost of sales are deducted from revenue. Cost of goods sold or Cost of Sales usually includes direct costs of producing goods, which were sold during the period of time in question, or cost of delivering the services incurred during the reporting period to provide these services.
 Difference between Revenue and Cost of goods sold or cost of sales results in Gross Profit.
Difference between Revenue and Cost of goods sold or cost of sales results in Gross Profit.
 The next is operating expenses, which are deducted from Gross Profit. Some examples of these expenses include rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, other general and administrative expenses. After these expenses are deducted from Gross profit, the result is operating profit or loss.
The next is operating expenses, which are deducted from Gross Profit. Some examples of these expenses include rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, other general and administrative expenses. After these expenses are deducted from Gross profit, the result is operating profit or loss.
 Finally, on the income statement any gains or losses from non-operating activities, such as investments, interest income or expenses, or the sale of assets, are reported. These items are added (if it is gain) or deducted (if it is loss) from Operating Profit (Loss) and the result is called Net Income (Net Loss), which is the last item on the income statement.
Finally, on the income statement any gains or losses from non-operating activities, such as investments, interest income or expenses, or the sale of assets, are reported. These items are added (if it is gain) or deducted (if it is loss) from Operating Profit (Loss) and the result is called Net Income (Net Loss), which is the last item on the income statement.
Income statement structure
The income statement usually has a standard structure and include the following items:
- Revenues: This section of the income statement reports total amount of revenue that the business earned during the period. Revenue can be earned from a variety of sources, such as sale of goods, provision of services, investment income. This part of income statement include revenue from the core business activities of a particular company
- Cost of Goods Sold: This section of the income statement reports the cost of goods sold or services provided during the period. Examples can be: cost of materials, labor, overhead associated with production of goods or provision of services.
- Gross Profit: This section of the income statement reports the difference between revenues and the cost of goods sold (services provided).
- Operating Expenses: This section of the income statement reports all expenses that the company incurred during the period, which are not directly related to the cost of goods sold (cost of services provided). Examples of such expenses can be salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, other general and administrative expenses.
- Operating Income: This section of the income statement reports the difference between gross profit and operating expenses. It is a result of business main operation for the reporting period.
- Other Income and Expenses: This section of the income statement reports any other income or expenses of the business incurred during the reporting period, which are not directly related to its core business operations. Examples of such other income (expenses) are interest income, interest expense, gains or losses from investments, other non-operating income or expenses.
- Income Before Taxes: This section of the income statement reports the total income (loss) that the company earned before accounting for taxes. Income before taxes is calculated by adding operating profit (loss) and result from other operations (other income (expenses).
- Income Tax Expenses: This section of the income statement reports the amount of tax expenses business incurred for the reporting period of time. It can cover actual income tax expenses and impact of deferred tax calculation (can be both income and expenses).
- Net Income: This section of the income statement reports the net income (net loss), which is the difference between Income Before Taxes and Income Tax Expenses.
 Such structure of income statement structure allows to provide clear and organized summary of a business financial performance over a specific period of time. It also shows results from the core and non-core operations of the business, which is very useful information, since it does allow to check, whether the business is capable to earn profits from its core operations.
Such structure of income statement structure allows to provide clear and organized summary of a business financial performance over a specific period of time. It also shows results from the core and non-core operations of the business, which is very useful information, since it does allow to check, whether the business is capable to earn profits from its core operations.
Main types of income statement
There are two main types of income statement:
- Single-Step Income Statement: this is a simple and straightforward format of the income statement, where reports total revenue are reported and total expenses are deducted from total revenue to get net income or net loss. This type of income statement does not separate operating and non-operating expenses. Subtotal of gross profit or operating profit are not provided.
- Multi-Step Income Statement: this is a more detailed format, which separates core (operating) and non-core (non-operating) activities of the business. This type of income statement provides such items, as gross profit and operating profit. It also reports other items, for example, interest income (expenses), gains (losses) on investments, income taxes.
Income statement importance
Check up for the main reasons, why income statement is a important financial statement. Income statement:
- Provides insight into financial performance: income statement provides valuable information about business financial performance over a specific period of time. By analyzing revenues, expenses, and profits, stakeholders can determine, if the company is generating profits or losses, and if its revenues are growing or declining.
- Helps with decision-making: income statement helps managers make informed and supported decisions by providing insight into the financial implications of various business decisions. For example, if a company is considering expanding into a new market, income statement can help assessing potential impact on revenues and expenses, and whether it would be profitable.
- Facilitates financial analysis: income statement is one of the three main financial statements used by investors, analysts, creditors and other users to assess company’s financial health. By comparing income statements from different periods or different companies, stakeholders can identify trends, evaluate performance, and make informed and supported investment decisions.
- Facilitates tax reporting: income statement is used to calculate company’s taxable income, which is reported to tax authorities. Accurate income statement helps ensuring that the company is paying the appropriate amount of taxes, and can help avoiding penalties and legal issues related to tax reporting.
 It is important to remember, that income statement is an essential tool to be used for the purpose of understanding business financial performance and making informed and supported business decisions. It is important for companies to prepare accurate and up-to-date income statements, regularly to ensuring, that they have a clear picture of their financial health.
It is important to remember, that income statement is an essential tool to be used for the purpose of understanding business financial performance and making informed and supported business decisions. It is important for companies to prepare accurate and up-to-date income statements, regularly to ensuring, that they have a clear picture of their financial health.
Issues & problems related to income statement
Although Income Statement is an important and useful financial statement, it is also related to certain issues and problems. Let’s explore some of them:
- Accounting errors: Income statements are prepared based on the company’s financial transactions and accounting records. If there are errors or omissions in the records, income statement may not accurately reflect the business financial performance.
- Timing differences: Income statements are prepared based on accrual accounting principle, which means that revenues and expenses are recognized, when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. This can lead to timing differences between, when the income statement shows revenue or expenses, and when the cash is actually received or paid.
- Non-recurring items: Non-recurring items, such as one-time gains or losses, unusual expenses, can distort income statement and make it difficult to assess the company’s ongoing financial performance.
- Estimates and assumptions: In certain cases, income statement may include estimates or assumptions, such as useful life of assets or the collectability of accounts receivable. If these estimates or assumptions are incorrect, they can impact the accuracy of the income statement.
- Inconsistent accounting policies: If a company changes its accounting policies, such changes can impact the comparability of income statements from different periods. This can make it difficult to assess business financial performance over time.
- Manipulation and fraud: Unfortunately, income statements can be manipulated or falsified to misrepresent a company’s financial performance. This can be done through fraudulent accounting practices or by intentionally misreporting financial transactions.
 Despite the above potential issues and problems, which are related to income statement, it’s important to ensure that income statements are prepared using accurate and consistent accounting records and policies, and that they are reviewed by qualified professionals to identify errors or inconsistencies. It’s also important to be aware of potential red flags, some of which were mentioned above, and investigate any potential discrepancies or inconsistencies.
Despite the above potential issues and problems, which are related to income statement, it’s important to ensure that income statements are prepared using accurate and consistent accounting records and policies, and that they are reviewed by qualified professionals to identify errors or inconsistencies. It’s also important to be aware of potential red flags, some of which were mentioned above, and investigate any potential discrepancies or inconsistencies.
Income statement relation to business
Income statement is one of thee there main and most important financial statements for businesses. It provides a snapshot of business financial performance over a specific period of time. Let’s explore, how income statement is related to business:
- Measuring profitability: One of the primary objectives of the income statement is measuring the profitability of a business. By comparing revenues and expenses, income statement shows, whether the company is generating a profit or a loss.
- Identifying trends: Income statement can be used to identify trends in the business financial performance. By comparing income statements from different periods, businesses can identify, whether their revenues and profits are growing or declining.
- Evaluating performance: Businesses can use income statements to evaluate their financial performance against industry standards or competitors. This can help identify the areas, where the business is performing well, as well as the areas, where improvements are needed.
- Informed and supported decision-making: The information provided in income statements can be used to make informed and supported business decisions. For example, a business may use income statement to evaluate the financial implications of expanding operations or investing in new projects.
- Facilitating financial planning: Income statements are often used as part of financial planning, as they provide important information for creating budgets, forecasts, and other financial projections.
 Income statement is an essential tool for businesses, as it helps them evaluating their financial performance, identifying areas for improvement, and making informed and supported decisions about their operations and investments.
Income statement is an essential tool for businesses, as it helps them evaluating their financial performance, identifying areas for improvement, and making informed and supported decisions about their operations and investments.
Income statement relation to accounting
Income statement is also closely related to the accounting are. Let’s explore these key relations:
- Accrual accounting: income statement is prepared applying accrual accounting principle, which implies recognition of revenues and expenses, when they are earned or incurred, rather than when the cash is received or paid. This principle provides more accurate picture of business financial performance over a specific period of time.
- Matching principle: income statement is also based on the matching principle, which requires, that expenses are matched with the revenues they generate. This means, that expenses are recognized in the same period as revenues they help generating. This ensures, that income statement accurately reflects business financial performance.
- Revenue recognition: income statement also implies revenue recognition rules and principles, which specify, when revenue has to be recognized for the accounting purposes. This principle requires, that revenue is recognized, when it is earned, regardless of when the cash is received and also when the other conditions for revenue recognitions are met.
- GAAP compliance: Income statement must comply with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), which represent a set of guidelines and standards for financial accounting and reporting purposes. Application of GAAP ensures, that income statement is prepared applying consistent and accurate accounting practices.
- Financial analysis: Income statement is also used for financial analysis, which is a key aspect of accounting. By analyzing income statements, accountants can identify trends, evaluate business financial performance, and make informed and supported decisions about a company’s financial health.
 Income statement is an essential component of accounting, since it provides important information about business financial performance over a specific period of time. Income statement is closely related to several accounting concepts and principles, and plays a critical role in the financial reporting and analysis.
Income statement is an essential component of accounting, since it provides important information about business financial performance over a specific period of time. Income statement is closely related to several accounting concepts and principles, and plays a critical role in the financial reporting and analysis.
Software, which can help with income statement preparation
Income statement preparation process can be done by using simple excel, however to speed up the process and insure its accuracy, and also speed of preparation, accounting software can be used. Some examples are provided further:
- QuickBooks: this is a popular accounting software, which includes income statement templates and features allowing users to create and customize income statements. QuickBooks also allows automated income and expense tracking, making it easier to create accurate income statements.
- Xero: this is another accounting software, which includes income statement templates and features for creating and customizing income statements. Xero also includes a wide range of reporting tools, which can be used to generate detailed financial reports, including income statements.
- FreshBooks: this is a cloud-based accounting software, which also, as two of the above mentioned examples, includes income statement templates and features for creating and customizing income statements. FreshBooks also includes time tracking and invoicing tools, making it easier to track and manage income and expenses.
- Zoho Books: this is one more example. It is cloud-based accounting software, which includes income statement templates and features for creating and customizing income statements. Zoho Books also includes a range of other accounting tools, such as inventory management and project management.
- Wave Accounting: Wave Accounting is a free accounting software, which includes income statement templates and features for creating and customizing income statements. Wave also includes a range of other accounting tools, such as invoicing and receipt scanning.
 The above mentioned accounting software programs can be helpful for businesses and individuals, who need to create income statements, speed up the process and ensure its accuracy. They provide a range of tools and features for creating and customizing income statements, and can help streamlining the accounting and financial reporting process.st of services provided), representing gross profit earned from core operations over the particular period of time.
The above mentioned accounting software programs can be helpful for businesses and individuals, who need to create income statements, speed up the process and ensure its accuracy. They provide a range of tools and features for creating and customizing income statements, and can help streamlining the accounting and financial reporting process.st of services provided), representing gross profit earned from core operations over the particular period of time.
Income statement vs balance sheet
The income statement and balance sheet are two of the main financial statements in accounting, and they serve different purposes. Here are some key differences between income statement and balance sheet:
- Purpose: income statement reports business financial performance over a specific period of time, typically a month, quarter, or year. Balance sheet, on the other hand, reports business financial position at a specific point in time, typically the end of a reporting period.
- Content: income statement reports revenues, expenses, and profits or losses, while the balance sheet reports assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Timeframe: income statement is prepared for a specific period of time, while balance sheet is prepared at a specific point in time.
- Format: income statement is typically presented as a single-page document which reports revenues, expenses, and profits or losses. Balance sheet is usually presented as a two-page format, which on one page reports assets, and on the other page – liabilities and equity.
- Use: income statement is used to evaluate business financial performance over a specific period of time. Balance sheet is used to evaluate business financial position at a specific point in time.
- Interdependence: income statement and balance sheet are interdependent, as the net income from the income statement is carried forward to the balance sheet as retained earnings.
Relation Between Income Statement and Balance Sheet
 In case Income Statement reports Net Income for the period, all the amount of Net Income or part of it can be distributed to the shareholders in the form of dividends. The remaining amount is transferred to the Balance Sheet Retained Earnings account, where profit not distributed to the shareholders or loss not covered by the shareholders is being accumulated.
In case Income Statement reports Net Income for the period, all the amount of Net Income or part of it can be distributed to the shareholders in the form of dividends. The remaining amount is transferred to the Balance Sheet Retained Earnings account, where profit not distributed to the shareholders or loss not covered by the shareholders is being accumulated.
If it is assumed that Net Income from the Income Statement is not distributed to the shareholders, in the picture below you can see how it is transferred to the Balance Sheet.
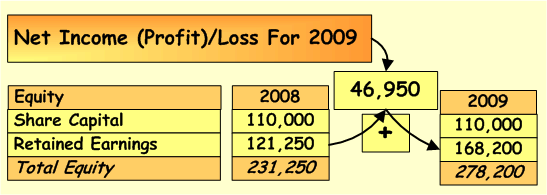
While income statement and balance sheet are both essential financial statements of the business, they serve different purposes and provide different information about business financial position and performance.
All topics to explore on Income Statement:
- Income Statement – what is an Income Statement?
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Income Statement Accounts
- Pro Forma Income Statement
- Income Statement Formula
- Contributuon Format Income Statement
- Single Step Income Statement
- Contributuon Margin Income Statement
- Statement of Comprehensive Income
- How to Prepare Income Statement?
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from Income Statement to AccountingCorner.org