What is revenue?
 Revenue is a gross increase owners’ capital or equity, which is resulted by the operations of the business.
Revenue is a gross increase owners’ capital or equity, which is resulted by the operations of the business.
Gross increase means that revenue amount is not decreased by any expenses, which were incurred to earn revenue.
The following transactions generate revenue for the business:
- sale of goods
- provision of services
- permission granted to use assets
- sale of assets, like plant assets
Most of revenues have certain features:
- Revenue arises from creating activities of a business
- It creates inflow of funds to the business, consequently increasing equity
- It is measured in the terms of money.
- It is always related to a particular accounting period, in which it is recognized and accounted for
- It is a result of a serious revenue generating activities performed by the business
- Business uses capital to earn a revenue
 There are three main revenue recognition methods:
There are three main revenue recognition methods:
- point of sale, or accrual basis
- cash basis
- installment
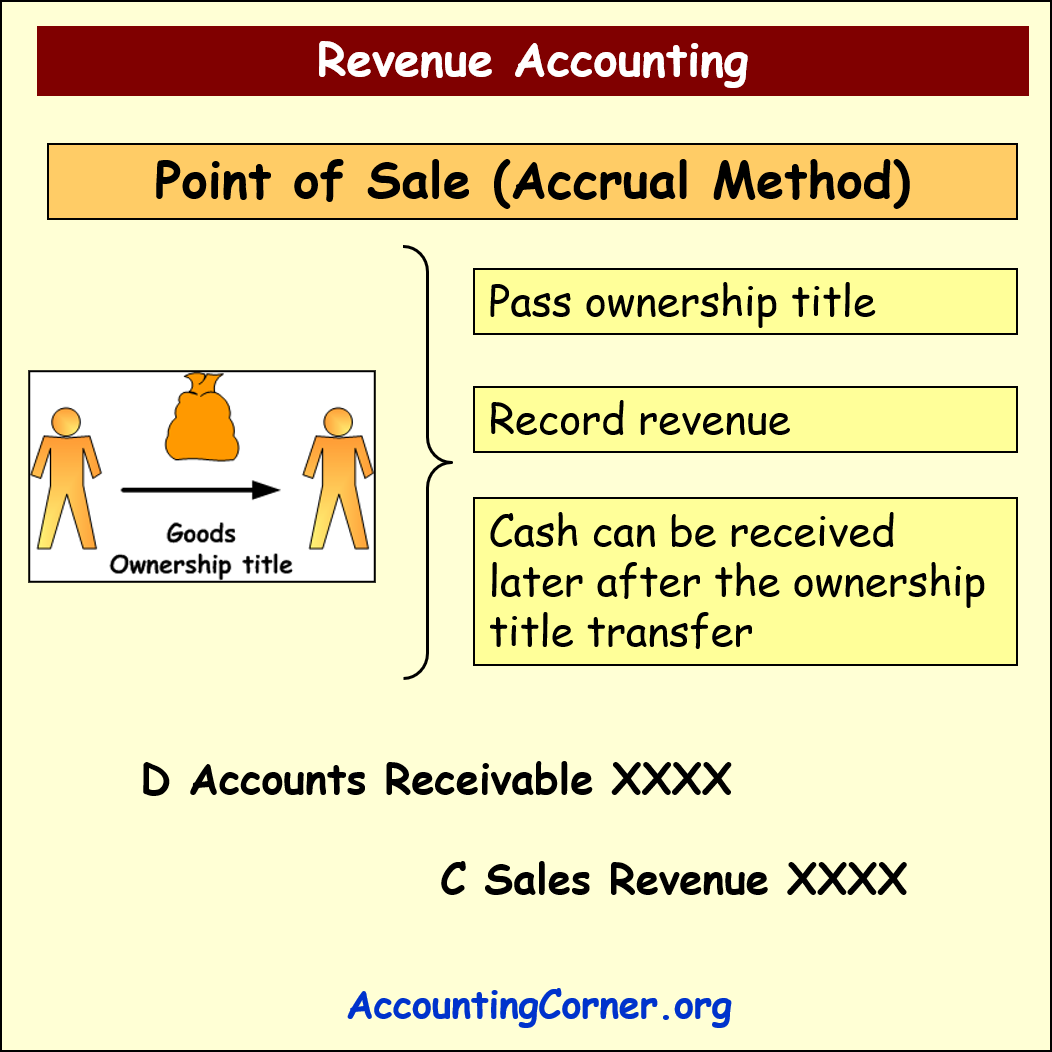
Point of Sale or Accrual Method
 Under this method revenues is recognized, when the ownership title to the goods is transferred from the seller to the customer. Revenue is recorded at the moment of this ownership transfer. Cash can be received later after the ownership title is transferred and this does not impact revenue recognition moment.
Under this method revenues is recognized, when the ownership title to the goods is transferred from the seller to the customer. Revenue is recorded at the moment of this ownership transfer. Cash can be received later after the ownership title is transferred and this does not impact revenue recognition moment.
The following accounting entries made:
- D Accounts Receivable (debt from the customer)
- _______C Sales Revenue
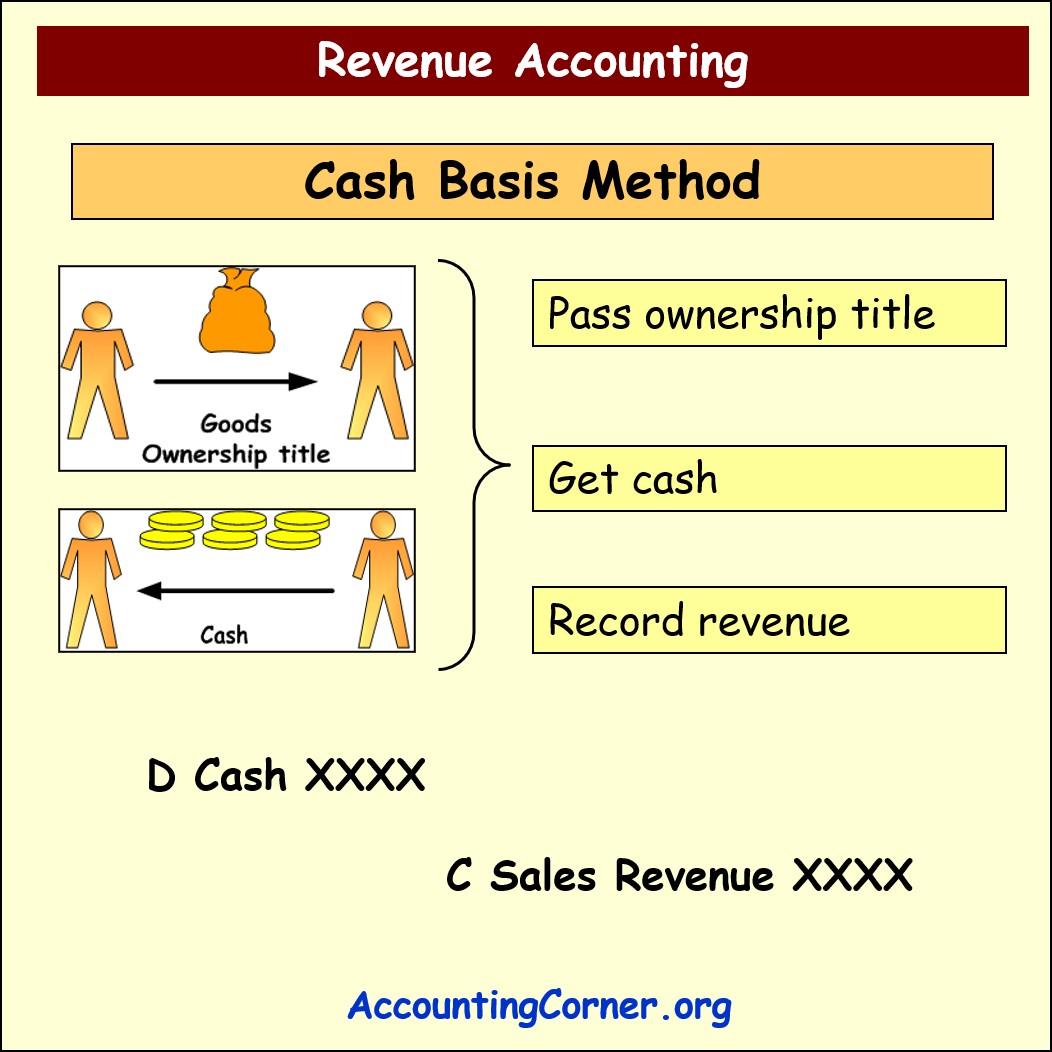
Cash Basis Method
 In case cash basis method for revenue recognition is applied, revenue is not recorded, when goods are sold and the ownership title is transferred from the seller to the customer. Basis for the revenue recognition and recording is the moment of cash receipt. Therefore revenue is recognized, when cash is received from the customer for the goods sold/services provided.
In case cash basis method for revenue recognition is applied, revenue is not recorded, when goods are sold and the ownership title is transferred from the seller to the customer. Basis for the revenue recognition and recording is the moment of cash receipt. Therefore revenue is recognized, when cash is received from the customer for the goods sold/services provided.
It might happened, that first the ownership title to the goods is transferred to the customer (or services are provided), and cash is received later. Sales revenue will be recognized only when cash is received.
The following accounting entries are made:
- D Cash
- _______C Sales Revenue
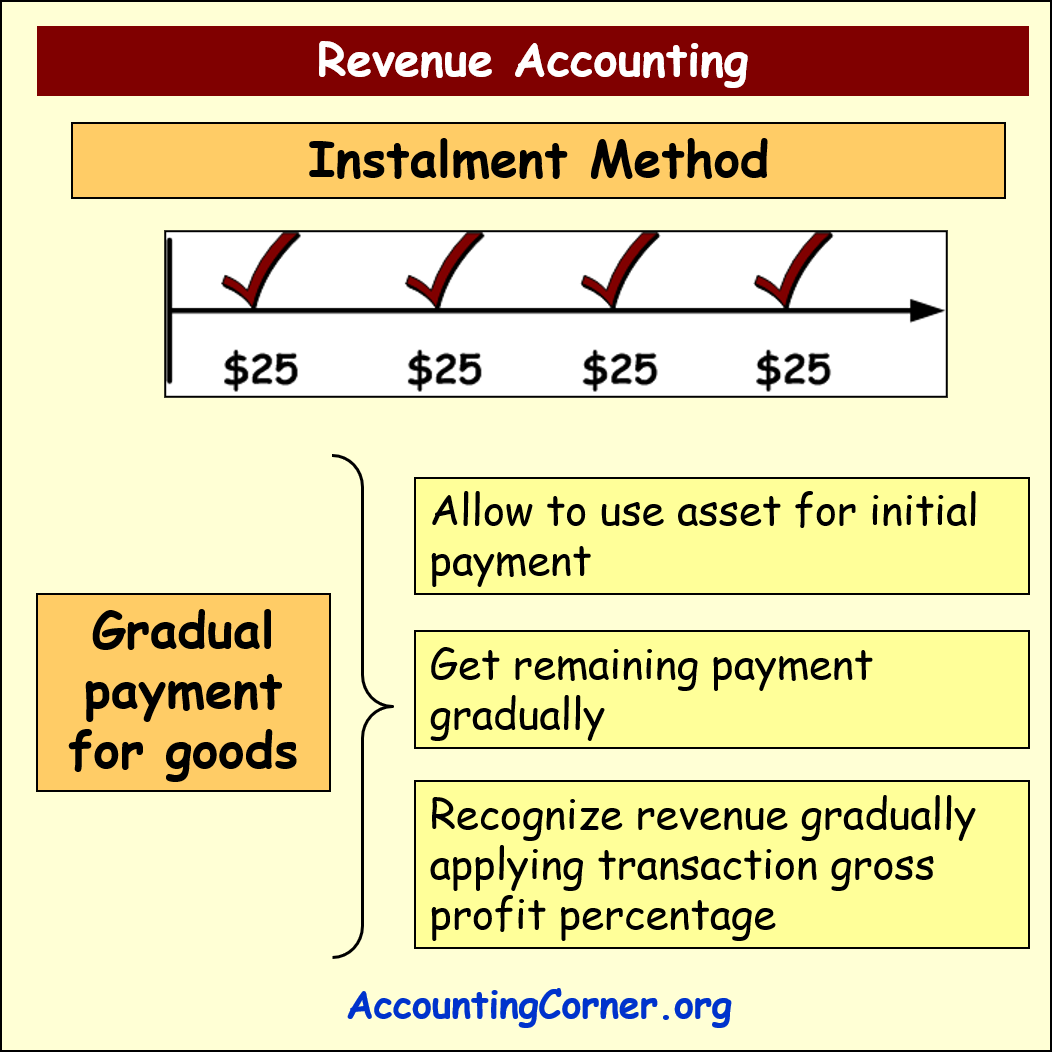
Installment Method
 Under the application of this method, revenue is gradually recognized gradually over the period of time
Under the application of this method, revenue is gradually recognized gradually over the period of time
The customer can get a right to use the asset in exchange for the initial payment. Remaining payment is received gradually and revenue is gradually recognized and recorded, applying transaction gross profit percentage.
Let’s explore an example. Let’s assume the business sells equipment:
- Sales price is 750 k$
- Cost is 562.5k $
- Gross profit amount is 187.5 k$
- Gross profit % is 25%
The customer will pay full price of the equipment over 4 years:
- 1st year – 150 k$
- 2nd year – 198 k$
- 3rd year – 242 k$
- 4th year – 160 k$
 This is a payment schedule agreed between the seller and the customer.
This is a payment schedule agreed between the seller and the customer.
In the table below revenue recognition process is explained
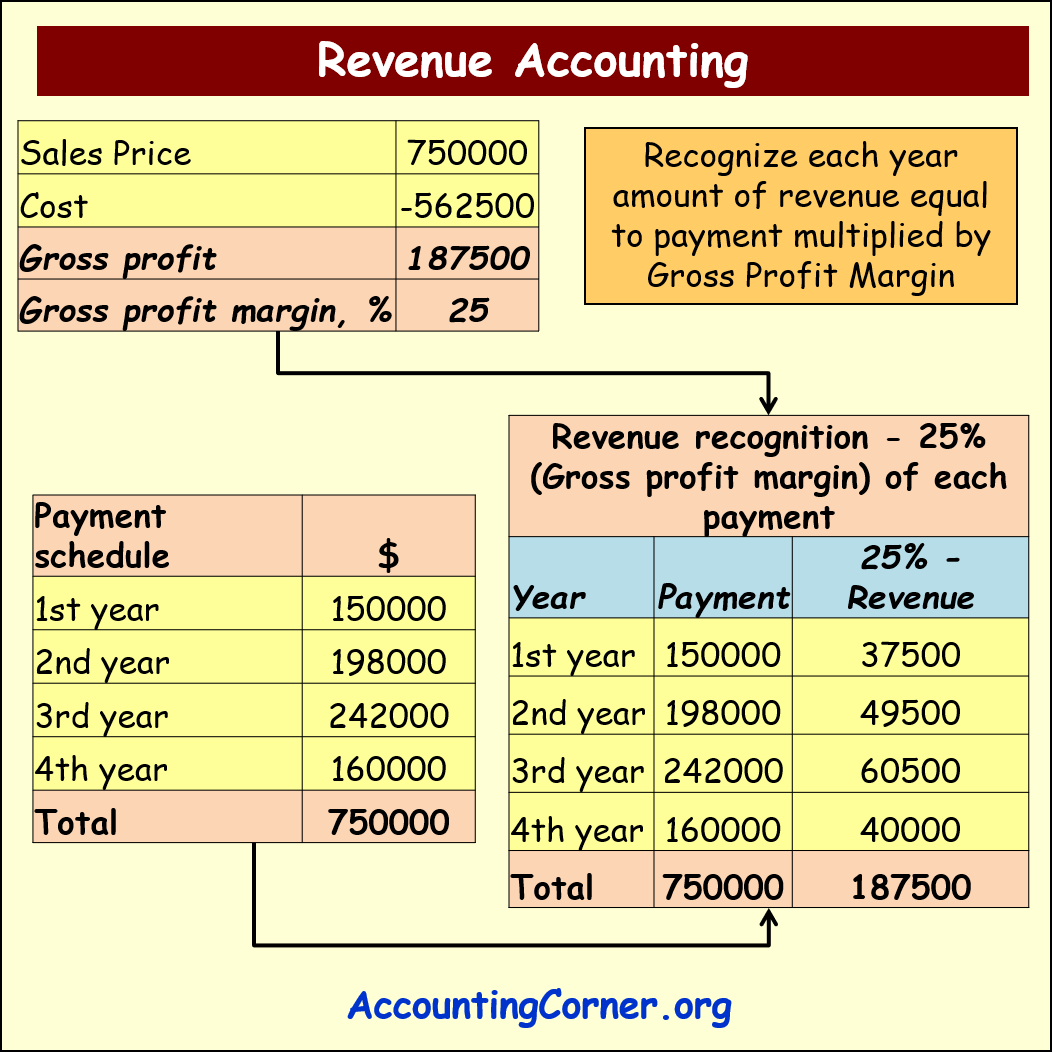
Each year the seller will recognize 25% (gross profit %) of gross profit on the sale, which is calculated on that year payment.
- In the 1st year it will be 150 k$*25%=37.5 k$
- In the 2nd year it will be 198 k$*25%=49.5 k$
- And so on
Over 4 year period of time the seller will recognize full amount of gross profit from the sale of equipment
All visual material on Revenue Accounting
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from Revenue Accounting to AccountingCorner.org