What are retained earnings?
Retained earnings are a crucial component of a corporation’s equity section, representing the portion of net profits retained within the business rather than distributed as dividends. These earnings reflect the accumulated income over time that can be reinvested into the business or distributed at the company’s discretion, impacting both the balance sheet structure and financing options.
Retained Earnings concept is one of the main accounting terms, which is essential for the purpose to understand:
- the structure of the Balance Sheet, and
- financing means, by which assets of a business are being financed
Retained Earnings Definition
Retained Earnings definition is closely related to the Equity definition
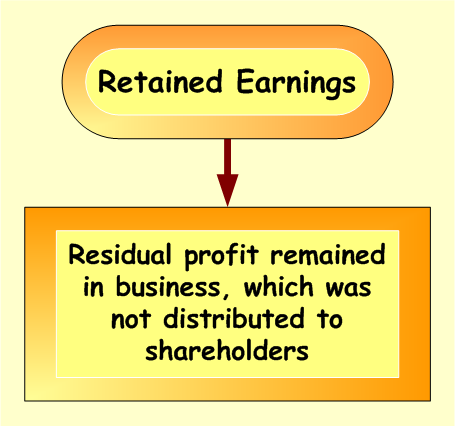
Residual means that:
- First, business has to pay back liabilities, and
- only afterwards, what is left, can be distributed to the shareholders
Therefore Equity is a difference between Assets and Liabilities and this also can be supported by the basic accounting equation, where:
Equity is comprised of:
- Share Capital – initial investment of the shareholders to the business, and
- Retained Earnings – net profit earned and remained in the business, which was not yet distributed to the shareholders. In case business makes loss, such loss is accumulated as not covered loss, which is negative and decreases the balance of Equity
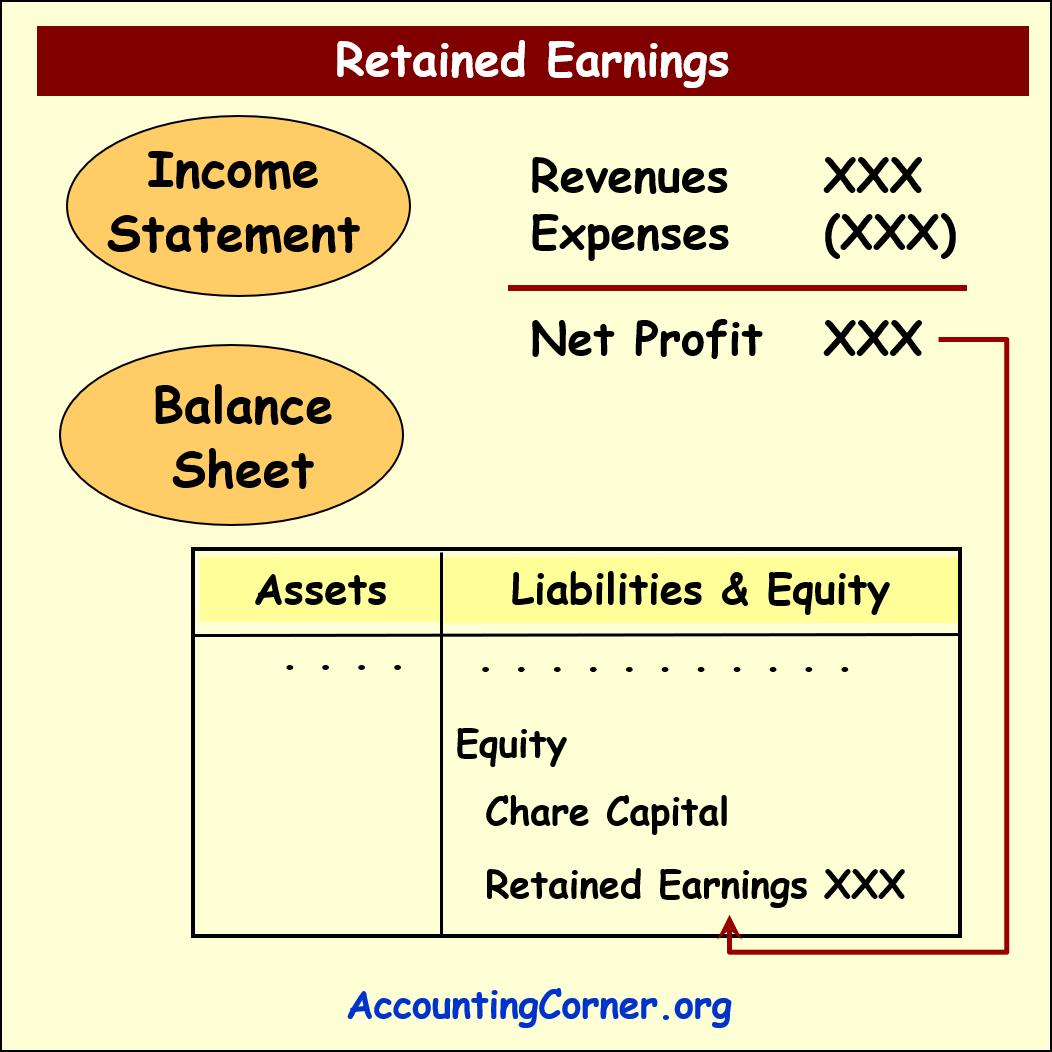
On the Balance Sheet these two items are indicated separately to demonstrate, how much shareholders invested into the business and how much the business has accumulated in not distributed profit (not covered loss) since start of the business operations.
Relation With Income Statement
In order to understand how to find Retained Earnings, the relation of it with the Income Statement should be demonstrated:
Let’s assume there is a company, which started its business on 1 January 2019. Shareholders invested $10,000 as cash at the start of business operations.
 Income Statement for the year 2019 is as follows (for simplicity purposes there are no taxes or interest expenses incurred):
Income Statement for the year 2019 is as follows (for simplicity purposes there are no taxes or interest expenses incurred):
- Revenue___________________25,000
- Cost Of Goods Sold_________(19,000)
- Gross Profit________________6,000
- Operating Expenses __________(3,000)
- Net Profit__________________3,000
Shareholders decided not to distribute dividends for the year 2019 and retain all the profit in the business.
 On the Balance Sheet at the Equity part there will be the following data:
On the Balance Sheet at the Equity part there will be the following data:
- Share Capital_______10,000
- Retained Earnings____3,000
- Total Equity________13,000
All the net profit from the Income Statement is transferred to the Balance Sheet as Retained Earnings, since this profit was retained in the business and not distributed to the shareholders.
Retained Earnings Meaning
Based on the above example, Retained Earnings represent residual net result (Profit or Loss) accumulated in the business.
 Retained Earnings balance can be positive, which does represent total net profit accumulated by the business and not distributed to the shareholders as dividends
Retained Earnings balance can be positive, which does represent total net profit accumulated by the business and not distributed to the shareholders as dividends
 Retained earnings balances can also be negative, which does represent total net loss accumulated by the business and not covered by the additional investments from the shareholders
Retained earnings balances can also be negative, which does represent total net loss accumulated by the business and not covered by the additional investments from the shareholders
In case the business is profitable during the particular accounting period, Net Profit is reported in the Income Statement. This amount increases Retained Earnings, if it is not distributed to the shareholders as dividends.
In case the business is not profitable during the particular accounting period, Net Loss will be reported in the Income Statement. This amount decreases Retained Earnings, if it is not covered by the shareholders by the additional investments.
 Retained Earnings balance accumulates starting from the beginning of the business operations, i.e. each accounting period Net Profit after dividends were paid, is accumulated and net profits for the later accounting periods are added up to this already accumulated balance.
Retained Earnings balance accumulates starting from the beginning of the business operations, i.e. each accounting period Net Profit after dividends were paid, is accumulated and net profits for the later accounting periods are added up to this already accumulated balance.
Retained Earnings balance for the first accounting period will be equal to Net Profit (Not Loss) for that accounting period after deducting of dividends paid out if any.
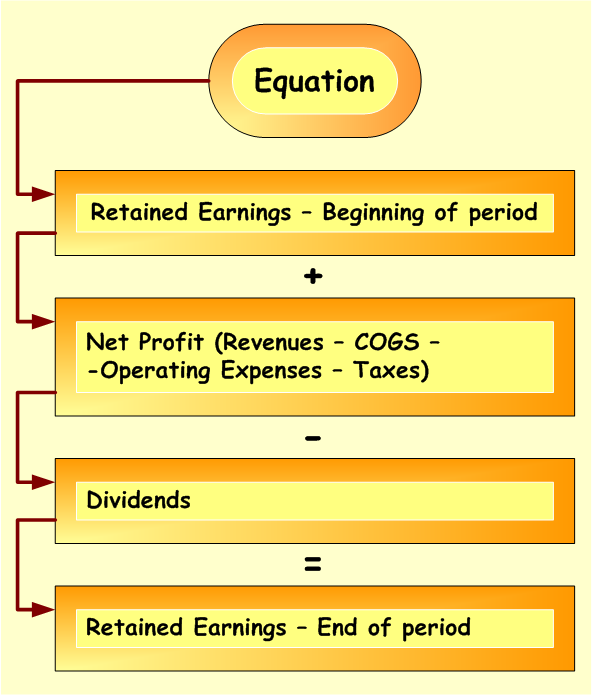
Exploring how to calculate retained earnings, check the following steps :
- First – start from the opening Retained Earnings balance, i.e. balance at the beginning of the accounting period. This figure is taken from the Balance Sheet Equity part. Prior accounting period Balance Sheet to be used
- Second – add up Net Profit for the accounting period. This amount is taken from the Income Statement for the current accounting period and it represents a difference between Revenues and all Expenses (Cost of Goods Sold or COGS, Operating Expenses, Taxes)
- Third – deduct from the result dividends paid if any. if there were not dividends paid during the current accounting period, there is nothing to deduct from the result obtained under the second step
After all the three above steps are made, we will get Retained Earnings balance at the end of the accounting period and it will be indicated separately under the Equity part on the Balance Sheet for the current period.
Ending retained earnings formula
The below equation is used to calculate ending balance of Retained Earnings
 Retained Earnings are a part of the Balance Sheet. Retained Earnings are reported under Equity part, since the accumulated balance does belong to the shareholders.
Retained Earnings are a part of the Balance Sheet. Retained Earnings are reported under Equity part, since the accumulated balance does belong to the shareholders.
Is retained earnings an asset? The answer is no, as it is a part of Equity
Statement of Retained Earnings
Retained Earnings Statement is a statement summarising changes in the Retained Earnings for a certain period of time.
Statement of Retained Earnings Format
The Statement of Retained Earnings reflects changes in retained earnings over a specific period, typically presented in the following format:
- Opening Balance: Starting balance from the previous period.
- Adjustments: Prior period adjustments, if any.
- Net Income or Loss: Current period net income added or net loss subtracted.
- Dividends: Dividends deducted if declared during the period.
- Closing Balance: Resultant retained earnings at period-end.
Here’s a sample statement for Uptown Co. for the year ending December 31, 2022:
- Retained Earnings, January 1: $20,000
- Net Income: $8,000
- Dividends: $2,500
- Retained Earnings, December 31: $25,500
The statement of retained earnings provides transparency on how profits are allocated within the business and retained for future growth.
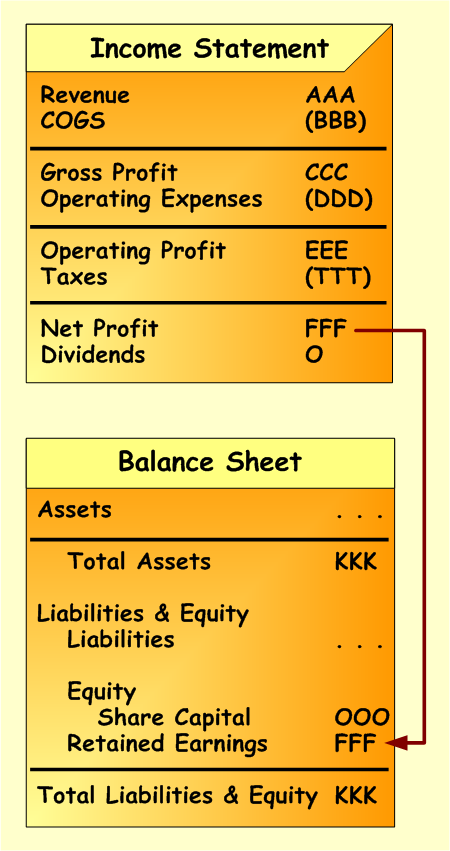
To compute Retained Earnings Net Profit from the Income Statement for the accounting period is taken. Then dividends are deducted (if any) and remaining balance is added the to the Retained Earnings balance on the Balance Sheet. The scheme below demonstrates this process.
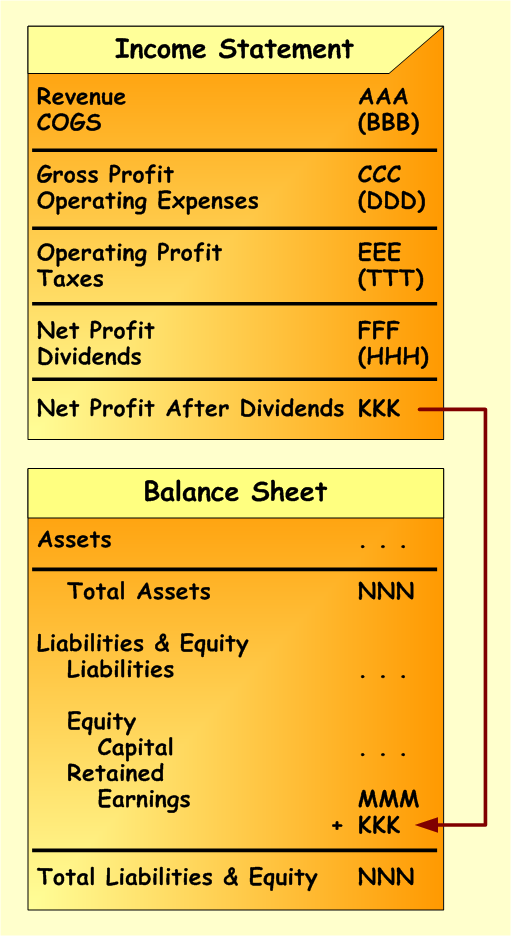
Worth to notice that Retained Earnings are presented under the Equity part on the Balance Sheet, since this amount belongs to the shareholders. It can be paid out as dividends during the later accounting periods.
Calculation of Retained Earnings also demonstrates the relationship between Income Statement and Balance Sheet.
Scheme below presents process of calculating Retained Earnings.
- First, we start from the Income Statement, where we need to calculate Net Profit.Net Profit is a difference between all revenues and all expenses. The below Income Statement being multiple step presents separate categories of revenues and expenses. Net Profit equals to FFF.
- Second, we need to know whether there were dividends announced and paid to the shareholders during the accounting period. The above calculation includes dividends. They are deducted from Net Profit amount, since they will not be included into the Retained Earnings balance. Amount of dividends – HHH.
- Third, we take Net Profit amount decreased by dividends (KKK) and add it up to the Retained Earnings balance on the Balance Sheet statement. The example already provides accumulated amount of Retained Earnings (MMM) from prior accounting periods. We need to add up to this amount current period increase in Retained Earnings (KKK).
After performing this process of calculating Retained Earnings, we can see closing balance, which is sum of prior periods amount (MMM) and current period amount (KKK).
Role in Financing and Equity Structure
Retained earnings serve as an internal source of funding for business growth, reducing reliance on external debt or additional shareholder investment. Retained earnings are accumulated profits that strengthen the company’s equity position on the balance sheet, impacting its overall financial health and investment attractiveness.
Presentation on the Balance Sheet
On the balance sheet, retained earnings appear in the equity section, separate from share capital. This distinction highlights how much profit has been reinvested versus initially invested by shareholders.
For example, a company with $30,000 in share capital and $18,000 in retained earnings shows that a significant portion of equity derives from business performance rather than initial investment.
Conclusion
Retained earnings offer a snapshot of the company’s retained profits over time, reinforcing its capability to fund future growth. A well-managed balance of retained earnings can indicate financial stability, signaling to stakeholders the company’s prudent approach toward profit reinvestment and dividend allocation.
By understanding and effectively managing retained earnings, companies can ensure they are equipped for sustainable development and value generation for shareholders.
The Most Popular Accounting & Finance Topics:
- Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Example
- Classified Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet Template
- Income Statement
- Income Statement Example
- Multi Step Income Statement
- Income Statement Format
- Common Size Income Statement
- Income Statement Template
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Flow Statement Example
- Cash Flow Statement Template
- Discounted Cash Flow
- Free Cash Flow
- Accounting Equation
- Accounting Cycle
- Accounting Principles
- Retained Earnings Statement
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings Formula
- Financial Analysis
- Current Ratio Formula
- Acid Test Ratio Formula
- Cash Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio
- Debt to Equity Ratio
- Debt Ratio
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Mortgage Calculator
- Mortgage Rates
- Reverse Mortgage
- Mortgage Amortization Calculator
- Gross Revenue
- Semi Monthly Meaning
- Financial Statements
- Petty Cash
- General Ledger
- Allocation Definition
- Accounts Receivable
- Impairment
- Going Concern
- Trial Balance
- Accounts Payable
- Pro Forma Meaning
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Cost of Goods Sold
- How to void a check?
- Voided Check
- Depreciation
- Face Value
- Contribution Margin Ratio
- YTD Meaning
- Accrual Accounting
- What is Gross Income?
- Net Income
- What is accounting?
- Quick Ratio
- What is an invoice?
- Prudent Definition
- Prudence Definition
- Double Entry Accounting
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit Formula
- What is an asset?
- Gross Margin Formula
- Gross Margin
- Disbursement
- Reconciliation Definition
- Deferred Revenue
- Leverage Ratio
- Collateral Definition
- Work in Progress
- EBIT Meaning
- FOB Meaning
- Return on Assets – ROA Formula
- Marginal Cost Formula
- Marginal Revenue Formula
- Proceeds
- In Transit Meaning
- Inherent Definition
- FOB Shipping Point
- WACC Formula
- What is a Guarantor?
- Tangible Meaning
- Profit and Loss Statement Template
- Revenue Vs Profit
- FTE Meaning
- Cash Book
- Accrued Income
- Bearer Bonds
- Credit Note Meaning
- EBITA meaning
- Fictitious Assets
- Preference Shares
- Wear and Tear Meaning
- Cancelled Cheque
- Cost Sheet Format
- Provision Definition
- EBITDA Meaning
- Covenant Definition
- FICA Meaning
- Ledger Definition
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- T Account / T Accounts
- Contra Account
- NOPAT Formula
- Monetary Value
- Salvage Value
- Times Interest Earned Ratio
- Intermediate Accounting
- Mortgage Rate Chart
- Opportunity Cost
- Total Asset Turnover
- Sunk Cost
- Housing Interest Rates Chart
- Additional Paid In Capital
- Obsolescence
- What is Revenue?
- What Does Per Diem Mean?
- Unearned Revenue
- Accrued Expenses
- Earnings Per Share
- Consignee
- Accumulated Depreciation
- Leashold Improvements
- Operating Margin
- Notes Payable
- Current Assets
- Liabilities
- Controller Job Description
- Define Leverage
- Journal Entry
- Productivity Definition
- Capital Expenditures
- Check Register
- What is Liquidity?
- Variable Cost
- Variable Expenses
- Cash Receipts
- Gross Profit Ratio
- Net Sales
- Return on Sales
- Fixed Expenses
- Straight Line Depreciation
- Working Capital Ratio
- Fixed Cost
- Contingent Liabilities
- Marketable Securities
- Remittance Advice
- Extrapolation Definition
- Gross Sales
- Days Sales Oustanding
- Residual Value
- Accrued Interest
- Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio
- Prime Cost
- Perpetual Inventory System
- Vouching
Return from Statement of Retained Earnings to AccountingCorner.org home